Evaluation of Preptin and other Biomarkers in Coronary Artery Disease Patients with and without Diabetes Mellitus
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad.6642350الكلمات المفتاحية:
Coronary artery disease، Lipid profile، Preptin، T2DM، Uric acidالملخص
Background: Preptin is an endocrine peptide with 34 amino acids. Conjugated with insulin, it is produced by β-cells from the pro-insulin-like growth factor 2 E-peptide. However, in addition to insulin, pancreatic hormone (Preptin) is released in response to elevated blood glucose levels. Preprint’s primary metabolic effect is to raise insulin synthesis, which is achieved through both an amplifying mechanism and a triggering route that is dependent on calcium signalling.
Objectives: To determine the Preptin in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) with and without Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
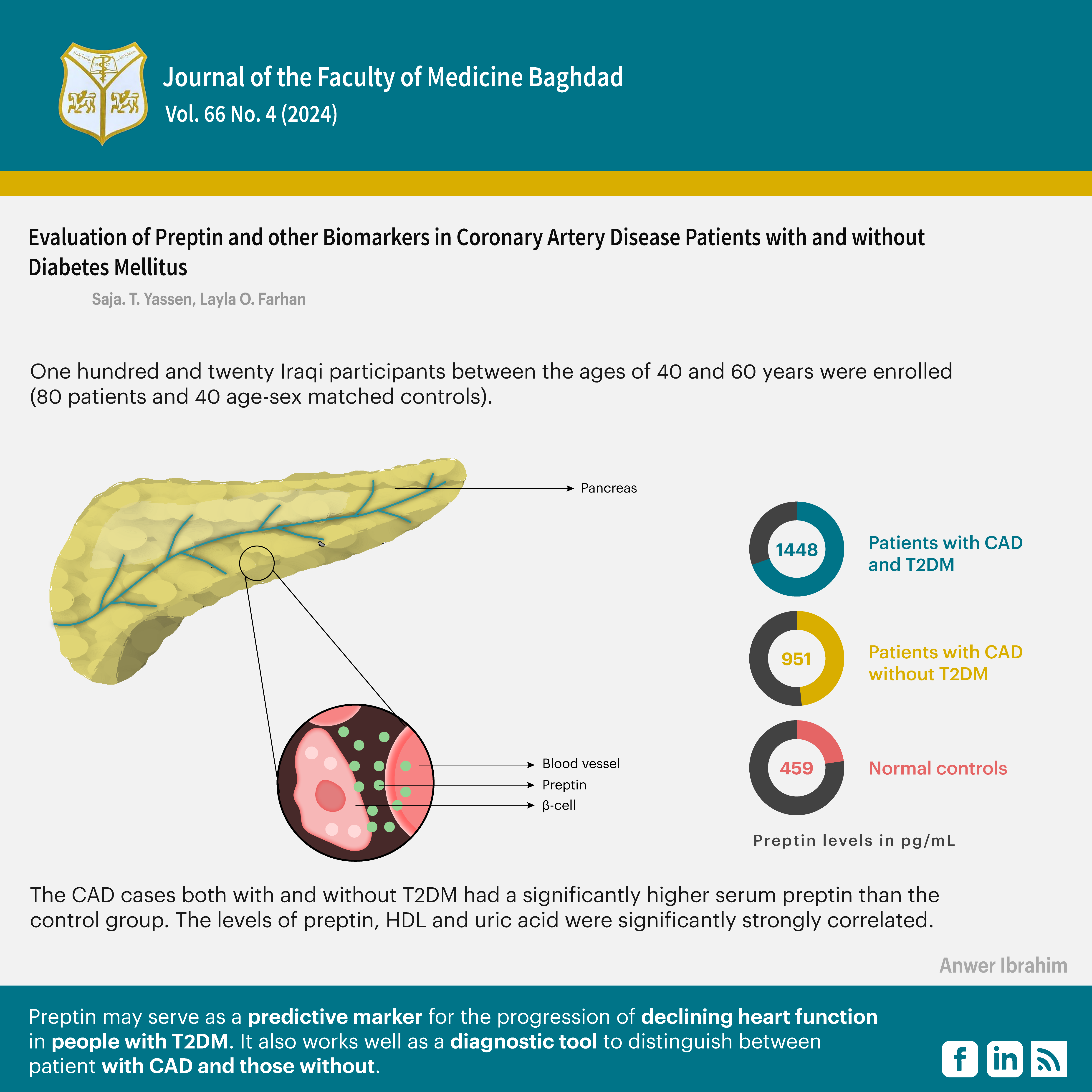
Methods: One hundred and twenty Iraqi participants between the ages of 40 and 60 years were enrolled (80 patients and 40 age-matched controls). The study took place between August and December 2023 at the Ibn Al-Bitar Centre for Cardiac Surgery in Baghdad, Iraq. The level of Preptin in patients with CAD with and without T2DM was evaluated. The biochemical tests performed on participants included fasting blood sugar (FBS), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low density lipoproteins (LDL), and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), high density lipoproteins (HDL), blood urea, serum creatinine, and uric acid. The waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and body mass index (BMI) were also computed. There was a significance level below 0.05 using the Mann-Whitney tests. A non-parametric method and the Spearman's rank coefficient were used to determine the significance of the correlation for the relationship between the two numerical variables. We determined the Preptin cut-off value by analysing the receiver operation characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results: The CAD cases both with and without T2DM had a significantly higher serum Preptin than the control group. The levels of Preptin, HDL, and uric acid were significantly strongly correlated. The Preptin ROC curve showed a clear cut-off value (>601.71, >818.10, and >694.71) with the area under the curve (AUA) (0.973, 0.996, and 0.985), respectively, when calculated in three groups: CAD without T2DM, CAD with T2DM, and both CAD groups together compared with the controls.
Conclusion: Preptin may serve as a predictive marker for the progression of declining heart function in people with T2DM. It also works well as a diagnostic tool to distinguish between patients with CAD and those without.
التنزيلات
المراجع
Wang H, Wang X, Cao Y, Han W, Guo Y, Yang G, et al. Association of polymorphisms of Preptin, irisin and adropin genes with susceptibility to coronary artery disease and hypertension. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(10):1-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000019365.
Ralapanawa U, Sivakanesan R. Epidemiology and the magnitude of coronary artery disease and acute coronary syndrome: a narrative review. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021;11(2):169-77. https://doi.org/10.2991/jegh.k.201217.001.
Ullah M, Wahab A, Khan SU, Zaman U, ur Rehman K, Hamayun S, et al. Stent as a novel technology for coronary artery disease and their clinical manifestation. Curr. Probl Cardiol. 2023;48(1):101415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101415.
Asada Y, Yamashita A, Sato Y, Hatakeyama K. Pathophysiology of atherothrombosis. Mechanisms of thrombus formation on disrupted atherosclerotic plaques. Pathol. Int. 2020;70(6):309–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/pin.12921.
Tohirova J, Shernazarov F. Atherosclerosis: causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Sci Innov. 2022;1(5):7–12. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6988810.
Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari S, Larrea-Sebal A, Siddiqi H, Uribe KB, et al. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21(17):1-34. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275.
Emad S, Saeed GT. Evaluation of Brain Stem Function in Diabetics with and Without Distal Symmetrical Polyneuropathy Using the Blink Reflex. JFacMedBaghdad. 2023;65(4):318-22. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.1987.
Abdulrahman AJ, Jabarah MAH, Najjar SA. Effects of liraglutide on weight control and blood pressure in type 2diabetes mellitus Iraqi patients. JFacMedBaghdad. 2022;64(4):227–32. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.6441971.
Taha BE, Majeed MJ. Estimation of Insulin Resistance in Obese Adults in Baghdad. J Fac Med Baghdad. 2023;65(4):335-40. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.2118.
Perumalsamy S, Huri HZ, Abdullah BM, Mazlan O, Wan Ahmad WA, Vethakkan SRDB. Genetic markers of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with coronary artery disease. Metabolites. 2023; 13(3): 1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030427.
Xu S, Ilyas I, Little PJ, Li H, Kamato D, Zheng X, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases and beyond: from mechanism to pharmacotherapies. Pharmacol .Rev. 2021;73(3):924–67. https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.120.000096.
Kałużna M, Pawlaczyk K, Schwermer K, Hoppe K, Yusuf Ibrahim A, Czlapka-Matyasik M, et al. Is Preptin a New Bone Metabolism Parameter in Hemodialysis Patients? Life. 2021;11(4):1-10. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11040341.
Elsaeed WFM, Abdel Rahman HM, Sasi NG, Zidan HEE. Serum Level of Preptin in Children with Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Relation to Diabetic Nephropathy. Egypt J Hosp. Med. 2021;84(1):2467–73. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejhm.2021.184670
Farhan AR, Rasheed MK. Estimation of Preptin Serum level, Insulin Resistance and other biochemical parameters in Pre-diabetic and Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus. HIV Nurs. 2023;23(2):196–201. https://doi.org/10.31838/hiv23.02.32.
Kashtl GJ, Abed BA, Farhan LO, Noori I, Salman ASD. A Comparative Study to Determine LDH Enzyme Levels in Serum Samples of Women with Breast Cancer and Women with Breast Cancer and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Med Chem Sci. 2023;6(4):883–90. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.
Abed BA, Al-AAraji SB, Salman IN. Estimation of Galanin hormone in patients with newly thyroid dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biochem Cell Arch. 2021; 21(1): 1317–21. https://connectjournals.com/03896.2021.21.1317.
Gao Y, Guo Y, Hao W, Meng J, Miao Z, Hou A, et al. Correlation Analysis and Diagnostic Value of Serum Homocysteine, Cystatin C and Uric Acid Levels with the Severity of Coronary Artery Stenosis in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2023; 16(1): 19–31. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.s411417.2023.8119.
Hussein RJA, Majid A. Evaluation the role of Preptin hormone and some biochemical parameters in Type2 diabetic patients with cardiovascular disease. Univ Thi-Qar J Sci. 2023; 10 (1):1-4. https://doi.org/10.32792/utq/utjsci/v10i1.1035.
Tahir NT, Al-Khateeb SMJ, Akram RS. Preptin as a Potential Marker in Iraqi Newly Diagnosed T2DM and T2DM with Cardiovascular Disease. J Contemp Med Sci. 2024; 10 (2):102-105. https://doi.org/10.22317/jcms.v10i2.1490.
Bhatia R, Bhatia A, Ganatara K. Correlation of body mass index and waist/hip ratio with severity of coronary artery disease. Int J Res Med Sci. 2022; 10(2): 388-92. https://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2326012.ijrms20220280.
Mohammed NUG, Gorial FI, Khaleel FM, Abed BA, Mutar SA, Farhan LO, et al. Role of Human β-Defensin-3 in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Observational Single-Center Study. AJMS. 2023; 5(1S):58-62. https://doi.org/10.54133/ajms.v5ilS.289.
Farhan LO, Abed BA, Dawood A. Comparison study between adipsin levels in sera of Iraqi patients with diabetes and neuropathy. Baghdad Sci J. 2023;20(3):726-33. https://dx.doi.org/10.21123/bsj.2022.7408.
Lefta NA, Abed AY, Abed BA. Estimation of asprosin levels in female Iraqi patients with type 2 diabetes and hypothyroidism. J Med Chem Sci. 2023;6(2):433–9. https://doi.org/10.26655/JMCHEMSCI.2023.2.23.
التنزيلات
منشور
إصدار
القسم
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2024 Saja T. Yassen, Layla O. Farhan

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


