دراسة نسيجية جديدة لتقييم التأثير المشترك لطعم عظام البقر وغذاء الملكات على التئام عظمة التجويف في نموذج الأرانب
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad3136الكلمات المفتاحية:
غذاء ملكات النحل، طُعم عظام البقر، التئام العظامالملخص
الخلفية: تم اقتراح مؤخرًا استخدام طعوم عظام الأبقار في تجاويف الاستخراج الطازجة لتقليل الانخفاض في حجم التلال. وقد أظهرت الدراسات التجريبية الحديثة أن غذاء ملكات النحل له خصائص مضادة للبكتيريا ومضادة للأكسدة ومضادة للأورام ومضادة للالتهابات مما يؤدي إلى توسع الأوعية الدموية وزيادة تكاثر الخلايا وتمايزها.
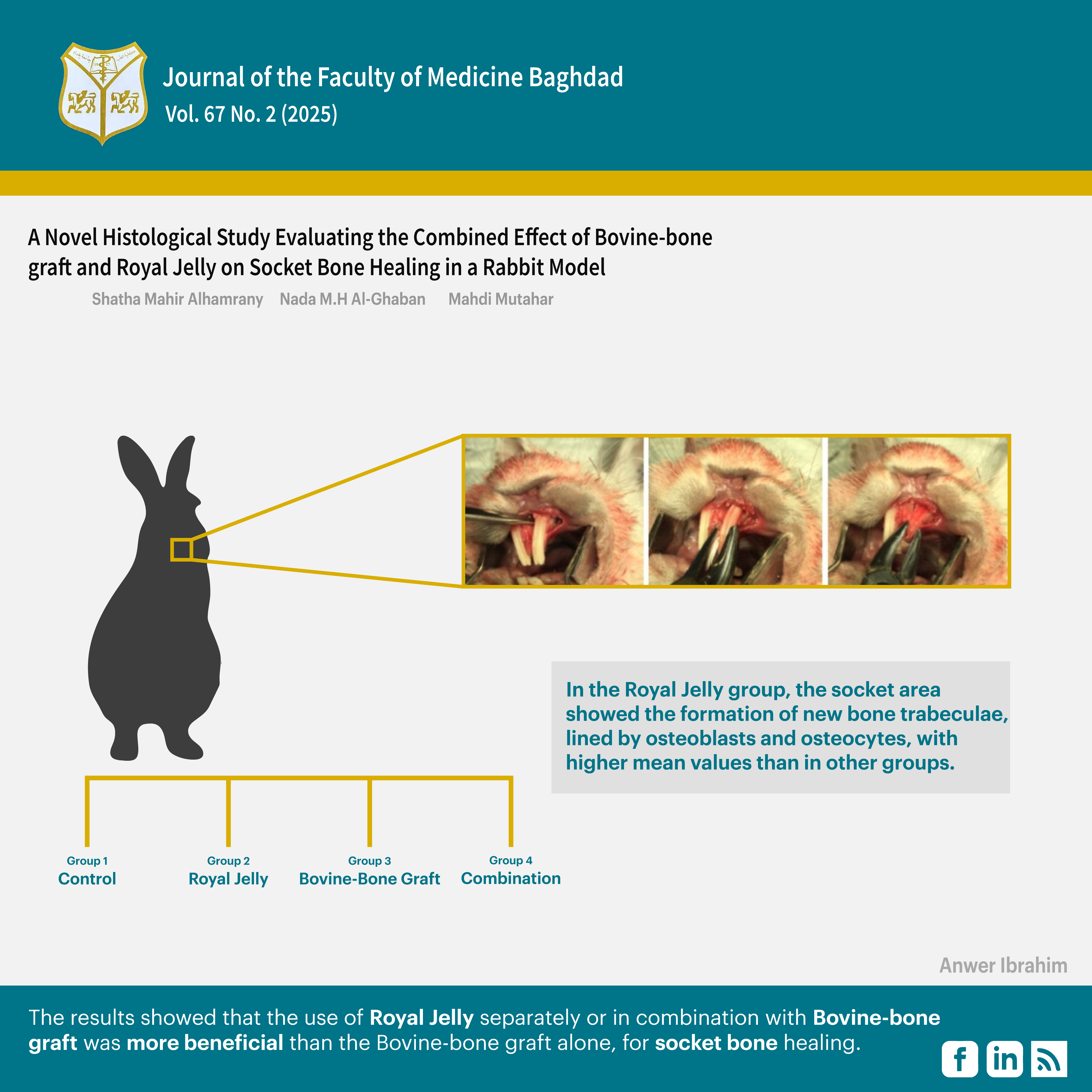
الغرض: كان الهدف من هذه الدراسة تقييم فعالية طعوم عظام الأبقار وغذاء ملكات النحل بشكل منفصل وبالاشتراك مع بعضها البعض في التئام عظم التجويف، حيث لا توجد دراسة سابقة حول تأثيرات هذا المزيج على التئام التجويف حتى الآن.
المواد والطرق: تم تقسيم ثمانية وأربعين أرنبًا ذكرًا (نيوزيلندا) بالتساوي إلى 4 مجموعات بعد استخراج القواطع المركزية العلوية تحت التخدير العام: المجموعة الأولى (المجموعة الضابطة)؛ المجموعة الثانية (غذاء ملكات النحل)، المجموعة الثالثة (طعوم عظام الأبقار)، المجموعة الرابعة (المجموعة المركبة). تمت دراسة النتائج نسيجيًا بعد أسبوعين وأربعة أسابيع من الجراحة. تم إجراء فحص نسيجي تحت المجهر الضوئي للجزء الملطخ بـ H&E.
النتائج: في مجموعة غذاء ملكات النحل، أظهرت منطقة التجويف تكوين عوارض عظمية جديدة مبطنة بالخلايا العظمية والخلايا العظمية بقيم متوسطة أعلى من المجموعات الأخرى. كشف التحليل النسيجي لمعلمة مساحة العظم الإسفنجي أن العوارض المعالجة بغذاء ملكات النحل والمزيج (طُعم عظمي تم تسليمه بغذاء ملكات النحل) سجلت قيمًا متوسطة أعلى من طُعم عظام البقر وحده ومجموعات التحكم.
الاستنتاج: أظهرت النتائج أن استخدام غذاء ملكات النحل بشكل منفصل أو بالاشتراك مع طُعم عظام البقر يمكن أن يكون أكثر فائدة من طُعم عظام البقر لالتئام عظم التجويف.
الكلمات المفتاحية: غذاء ملكات النحل، طُعم عظام البقر، عوارض الاستخراج، التئام العظام، الأرانب
المراجع
1. 1. Nanci A. Ten Cate's Oral Histology: Development, Structure, and Function. 10th ed. 2024. ISBN: 978-0-323-79895-2.
2. Atieh MA, Alsabeeha NHM, Payne AGT, Ali S, Faggion CM Jr, Esposito M. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: alveolar ridge preservation techniques for dental implant site development. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;4:CD010176. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010176.pub3
3. Kim S, Kim SG. Advancements in alveolar bone grafting and ridge preservation: a narrative review on materials, techniques, and clinical outcomes. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg. 2024;46:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-024-00425-w
4. Kamil NB, Al-Ghaban NH, Amery A. Osseointegration effects of whey protein (histological and histomorphological observations): An experimental study on rabbits. Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry,2023, Vol.35, No.3. https://doi.org/10.26477/jbcd.v35i3.3449
5. Madi M, Almindil I, Alrassasi M, Alramadan D, Zakaria O, Alagl AS. Cone-beam computed tomography and histological findings for socket preservation techniques using different grafting materials: a systematic review. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14:282. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14050282
6. Khalel AM, Fadhil E. Histological and immunohistochemical study of osteocalcin to evaluate the effect of local application of Symphytum officinale oil on bone healing in rats. Diyala J Med.2020;18(2):June2020. https://doi.org/10.26505/DJM.18024981002
7. Abd Alrazaq M, Al-Ghaban NM. Histological evaluation of the effect of local application of grape seed oil on the healing process of extracted tooth socket in rabbits. 2019. https://doi.org/10.26505/DJM.17024670515
8. Alsaeed MA, Al-Ghaban NM, Karaibrahimoğlu A. The influence of Simvastatin carried by chitosan nanoparticle on bone regeneration using Masson's Trichrome histochemical stain. Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry. 2023;35(4). https://doi.org/10.26477/jbcd.v35i4.3516
9. Temmerman A, Cortellini S, Van Dessel J, De Greef A, Jacobs R, Dhondt R, et al.. Bovine-derived xenograft in combination with autogenous bone chips versus xenograft alone for the augmentation of bony dehiscences around oral implants: a randomized, controlled, split-mouth clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2020;47:110-119. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.13209
10. Kamadjaja DB, Satriyo H, Setyawan A, Lesmaya YD, Safril JW, Sumarta NPM, et al.. Analyses of bone regeneration capacity of freeze-dried bovine bone and combined deproteinized-demineralized bovine bone particles in mandibular defects: the potential application of biological forms of bovine-bone filler. Eur J Dent.2022;16:403-413. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1736291
11. Hattori H, Nomoto H, Fukumitsu S, Mishima S, Furukawa S. Royal jelly and its unique fatty acid, 10-hydroxy-trans-2-decenoic acid, promote neurogenesis by neural stem/progenitor cells in vitro. Biomed Res. 2007;28(5):261-6. https://doi.org/10.2220/biomedres.28.261
12. Álvarez S, Contreras-Kallens P, Aguayo S, Ramírez O, Vallejos C, Ruiz J, et al.. Royal jelly extracellular vesicles promote wound healing by modulating underlying cellular responses. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.2023;31:541-552, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2023.02.008
13. Bagameri L, Botezan S, Bobis O, Bonta V, Dezmirean DS. Molecular insights into royal jelly anti-inflammatory properties and related diseases. Life. 2023;13(7):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13071573
14. Collazo N, Carpena M, Nuñez-Estevez B, Otero P, Simal-Gandara J, Prieto MA. Health promoting properties of bee royal jelly: food of the queens. Nutrients. 2021;13:543.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020543
15. Riggs GG, Boaz ARZI, Cissell DD, Hatcher DC, Kass PH, Zhen A, et al.. Clinical application of cone-beam computed tomography of the rabbit head: Part 1 - Normal dentition.Front Vet Sci. 2016;3:6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2016.00093
16. Plumb DC. Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook. 6th ed. Blackwell Publishing; 2008. p. 515
17. Al-Ghaban NM, Jasem GH. Histomorphometric evaluation of the effects of local application of red clover oil (Trifolium pratense) on bone healing in rats. Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry. 2020;32(2):June. https://doi.org/10.26477/jbcd.v32i2.2891
18. Vieira A, Repeke CE, Ferreira Júnior S de B, Colavite PM, Biguetti CC, Oliveira RC, et al.. Intramembranous bone healing process subsequent to tooth extraction in mice: micro-computed tomography, histomorphometric and molecular characterization. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0128021. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0128021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128021
19. Hattori S, Omi N. The effects of royal jelly protein on bone mineral density and strength in ovariectomized female rats. Phys Act Nutr. 2021;25(2):33-37.
https://doi.org/10.20463/pan.2021.0013
20. Bigham-Sadegh A, Torkestani HS, Sharifi S, Shirian S. Effects of concurrent use of royal jelly with hydroxyapatite on bone healing in a rabbit model: radiological and histopathological evaluation. 2020;6:e04547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04547
21. Ozan F, Çörekçi B, Toptaş O, Halicioğlu K, Irgin C, Yilmaz F, et al.. Effect of royal jelly on new bone formation in rapid maxillary expansion in rats. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2015;20:e651. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.20581
22. You MM, Chen YF, Pan YM, Liu YC, Tu J, Wang K, et al.. Royal jelly attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in BV-2 microglial cells through modulating NF-κB and p38/JNK signaling pathways. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:7834381. doi:10.1155/2018/7834381.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7834381
23. de Freitas NR, Guerrini LB, Esper LA, Sbrana MC, Dos Santos CCV, de Almeida ALPF. Photobiomodulation and inorganic bovine bone in guided bone regeneration: histomorphometric analysis in rats. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14:281. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb14050281
24. Ceccarelli G, Presta R, Benedetti L, Cusella De Angelis MG, Lupi SM, Rodriguez YBR. Emerging perspectives in scaffold for tissue engineering in oral surgery. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:4585401. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4585401
25. Stacchi C, Lombardi T, Ottonelli R, Berton F, Perinetti G, Traini T. New bone formation after transcrestal sinus floor elevation was influenced by sinus cavity dimensions: a prospective histologic and histomorphometric study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29:465-79. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13144
26. Georgeanu VA, Gingu O, Antoniac IV, Manolea HO. Current options and future perspectives on bone graft and biomaterials substitutes for bone repair, from clinical needs to advanced biomaterials research. Appl Sci. 2023;13:8471. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148471
27. Ibrahim FM, Ghani BA, Fatalla AA. Histological evaluation of the effect of local application of Punica granatum seed oil on bone healing. Int J Biomater. 2022;2022:4266589. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4266589
28. Oryan A, Meimandi-Parizi A, Sayahi E, Bigham-Sadegh A. Royal jelly: a novel biological product in healing of a critical bone defect model in rat. EC Orthopaedics. 2019;10(4):216-27.
التنزيلات
منشور
إصدار
القسم
الفئات
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2025 Shatha M. Alhamrany, Nada M.H Al-Ghaban, Mahdi Mutahar

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


