تأثير هرمون الغريلين في المصل على مؤشر كتلة الجسم لدى الأطفال المصابين بمرض السكري من النوع الأول
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad2769الكلمات المفتاحية:
الغريلين، داء السكري من النوع الأول ، جلوكوز الدم الصائم، الهيموجلوبين السكريالملخص
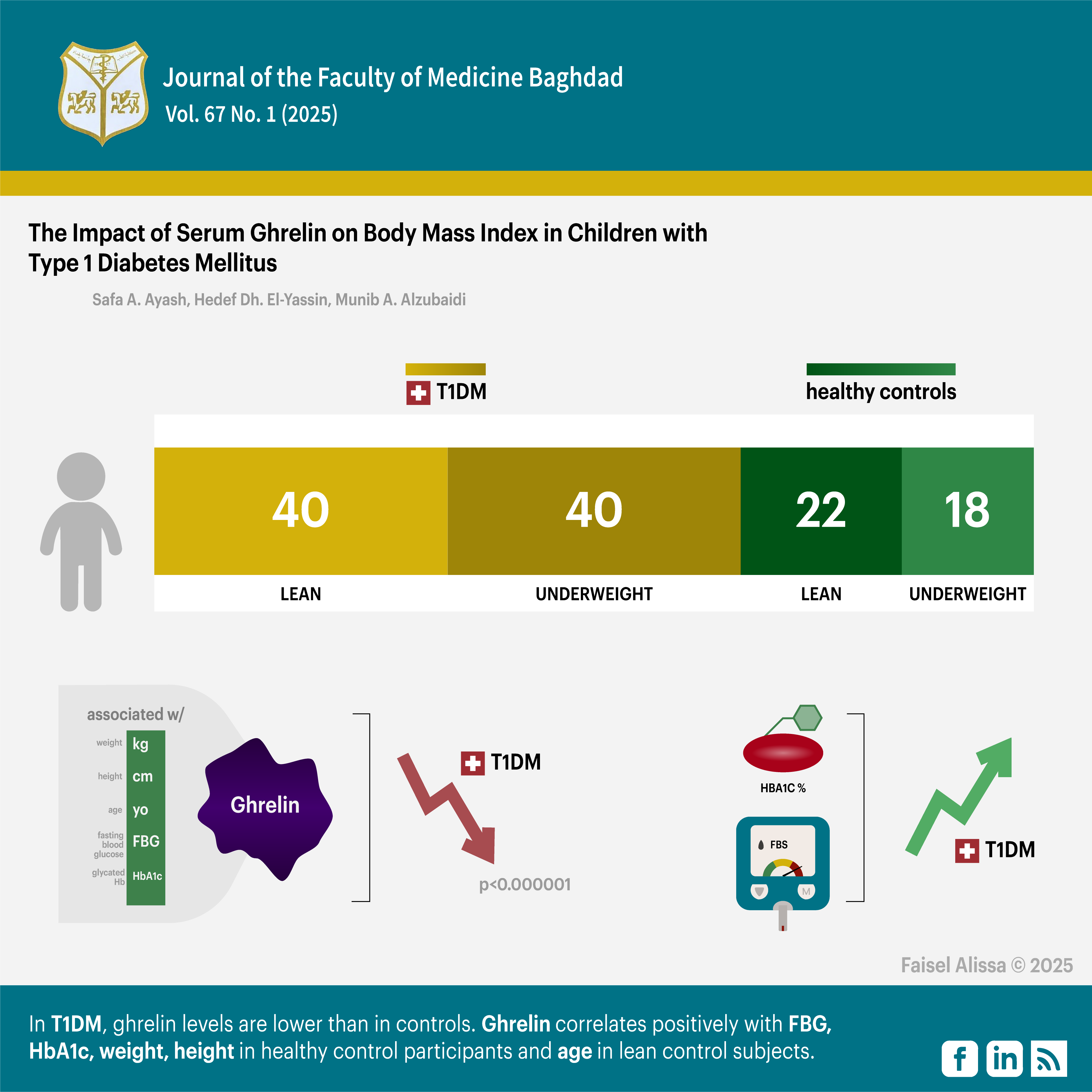
الملخص: يتوقف إنتاج الأنسولين في خلايا بيتا البنكرياسية عند الأشخاص المصابين بمرض السكري من النوع الأول، وهو مرض غدي يحدث غالبًا بسبب تلف المناعة الذاتية. ويمكن أن يسبب فقدان الوزن. يتحكم توازن الطاقة في إفراز هرمون الغريلين، وهو هرمون ببتيدي تصنعه الخلايا الصماء المعوية الموجودة في الغدد المؤكسدة لقاع المعدة. الموضوعات والمواد والطريقة: شملت هذه الدراسة 120 فردًا من الأطفال تتراوح أعمارهم بين (2-14) عامًا. تم تقسيمهم إلى أربع مجموعات. المجموعة الأولى تحتوي على 40 مريضًا نحيفين مصابين بمرض السكري من النوع الأول، مع نسبة مئوية من مؤشر كتلة الجسم ≥ 85، والمجموعة الثانية تحتوي على 40 مريضًا يعانون من نقص الوزن مصابين بمرض السكري من النوع الأول مع نسبة مئوية من مؤشر كتلة الجسم ≥ 5. تحتوي المجموعة على 40 طفلًا سليمًا وأعمارهم مطابقة للمرضى مقسمة إلى (المجموعة الثالثة، مجموعة التحكم النحيفة مع مؤشر كتلة الجسم أقل من 85 مئوية. المجموعة التي بلغ عددها 22، وأربع مجموعات، مجموعة التحكم في الوزن الناقص مع مؤشر كتلة الجسم ≥ 5 مئوية، تتكون من 18 طفلًا سليمًا يعانون من نقص الوزن كمجموعة تحكم. تم تحليلهم من أجل الجلوكوز في مصل الصيام، والجريلين، وHbA1c. النتائج: كانت مستويات الجريلين في المجموعة الضابطة (النحيفة ونحيفة الوزن) أعلى من تلك الموجودة في المرضى المصابين بداء السكري (النحيفة ونحيفة الوزن). كما تم العثور على جلوكوز الدم السريع (FBG) في مجموعة السكري النحيفة. وبالمثل، كانت مجموعة السكري الناقص الوزن أعلى من تلك التي لوحظت في مجموعتي التحكم النحيفة والتحكم في الوزن الناقص. بالنسبة لـ HbA1c٪، مجموعة السكري النحيفة. أظهرت مجموعة السكري الناقص الوزن متوسطًا أعلى لـ HbA1c٪. في المقابل، كان لدى مجموعتي التحكم النحيفة والتحكم في الوزن الناقص متوسطًا أقل بشكل ملحوظ قيم HbA1c%. الخلاصة: وجد لدى المريض مستويات منخفضة بشكل ملحوظ من هرمون الغريلين مقارنة بالضوابط الصحية، كما وجد ارتباط إيجابي بين الغريلين وHbA1c، وسكر الدم، والوزن، والطول في الأفراد الأصحاء (النحيفين ونحيفي الوزن) والعمر في الأفراد النحيفين. ولم يتم العثور على ارتباط بين الغريلين والمريض (مرض السكري من النوع الأول
التنزيلات
المراجع
Nekoua MP, Alidjinou EK, Hober D. Persistent coxsackievirus B infection and pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022;18(8):503–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-022-00688-1 . Epub 2022 Jun 1. PMID: 35650334; PMCID: PMC9157043.
2. Mobasseri M, Shirmohammadi M, Amiri T, Vahed N, Fard HH, Ghojazadeh M. Prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes in the world: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heal Promot Perspect. 2020;10(2):98. https://doi.org/10.34172/hpp.43143. PMID: 32296622; PMCID: PMC7146037.
3. Mihalache L, Gherasim A, Niţă O, Ungureanu MC, Pădureanu SS, Gavril RS, et al. Effects of ghrelin in energy balance and body weight homeostasis. Hormones [Internet]. 2016;15(2):186–96. Available from: https://doi.org/10.14310/horm.2002.1672
4. Solomou S, Korbonits M. The role of ghrelin in weight-regulation disorders: Implications in clinical practice. Hormones. 2014;13(4):458–75. https://doi.org/10.14310/horm.2002.1551 . PMID: 25555181.
5. NoorAldeen ZE, EL-Yassin HD, Al Naddawi MN. Suppression of Insulin Secretion by Ghrelin and The Deterioration of Glucose Tolerance in Healthy Children. J Fac Med Baghdad [Internet]. 2013 Jul 1;55(3 SE-Articles):254–7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.553626
6. Rhea EM, Salameh TS, Gray S, Niu J, Banks WA, Tong J. Ghrelin transport across the blood–brain barrier can occur independently of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Mol Metab. 2018;18:88–96 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2018.09.007 . Epub 2018 Sep 24. PMID: 30293893; PMCID: PMC6308033.
7. Razak Abdl Ghani ZA, Mukhtar RS, Fadhel MA, Turki KM. Impact of weight loss achieved through gastric sleeve surgery with circulating level of ghrelin hormone in obese Iraqi subjects. J Fac Med Baghdad [Internet]. 2015 Apr 5;57(1 SE-Articles):50–3. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.571308
8. Ramasamy I. Physiological Appetite Regulation and Bariatric Surgery. J Clin Med. 2024;13(5):1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13051347 . PMID: 38546831; PMCID: PMC10932430.
9. Marcovecchio ML, Hendriks AEJ, Delfin C, Battelino T, Danne T, Evans ML, et al. The INNODIA Type 1 Diabetes Natural History Study: a European cohort of newly diagnosed children, adolescents and adults. Diabetologia. 2024;67(6):995–1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-024-06124-5 . Epub 2024 Mar 22. PMID: 38517484; PMCID: PMC11058619.
10. Keşim DA, Kelle M, Aşır F, Kaya HK, Diken H, Gökdemir GŞ, et al. Investigation of the relationship between plasma ghrelin levels and muscle atrophy in experimental diabetic rats. Pol J Vet Sci. 2024;279–88. Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences
https://doi.org/10.24425/pjvs.2024.149358
11. Polkowska A, Szczepaniak I, Bossowski A. Assessment of serum concentrations of ghrelin, obestatin, omentin‐1, and apelin in children with type 1 diabetes. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016(1):8379294.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8379294 . Epub 2016 Jan 19. PMID: 26904686; PMCID: PMC4745415.
12. Shaikh I, Ibrahim MN, Laghari T, Chachar S, Riaz M, Ahmed SH. Comparison of Body Composition Bio Electrical Impedance Analysis of Type-1 Diabetes vs. Non-Diabetes in Children and Adolescent. Liaquat Natl J Prim Care. 2024; https://doi.org/10.37184/lnjpc.2707-3521.6.9
13. De Keukelaere M, Fieuws S, Reynaert N, Vandoorne E, Kerckhove K Vande, Asscherickx W, et al. Evolution of body mass index in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pediatr. 2018;177:1661–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-018-3224-9 . Epub 2018 Aug 9. PMID: 30091111.
14. Rahman MS, Hossain KS, Das S, Kundu S, Adegoke EO, Rahman MA, et al. Role of insulin in health and disease: an update. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126403 . PMID: 34203830; PMCID: PMC8232639.
15. Ochocińska A, Wysocka-Mincewicz M, Świderska J, Cukrowska B. Selected serum markers associated with pathogenesis and clinical course of type 1 diabetes in pediatric patients—The effect of disease duration. J Clin Med. 2023;12(6):2151. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062151 . PMID: 36983153; PMCID: PMC10051659.
16. Reed J, Bain SC, Kanamarlapudi V. The Regulation of Metabolic Homeostasis by Incretins and the Metabolic Hormones Produced by Pancreatic Islets. Diabetes, Metab Syndr Obes. 2024;2419–56. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S415934 . PMID: 38894706; PMCID: PMC11184168.
17. Li J, Huang P, Xiong J, Liang X, Li M, Ke H, Chen C, Han Y, Huang Y, Zhou Y, Luo Z, Feng D, Chen C. Serum levels of ghrelin and LEAP2 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: correlation with circulating glucose and lipids. Endocr Connect. 2022 May 27;11(5):e220012. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-22-0012 . PMID: 35521798; PMCID: PMC9175609.
18. Lopes KG, Silva VL da, Lopes F de AM, Bouskela E, Souza M das GC de, Kraemer-Aguiar LG. Ghrelin and glucagon-like peptide-1 according to body adiposity and glucose homeostasis. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2023;67(4):e000611. https://doi.org/10.20945/2359-3997000000611 . PMID: 37252699; PMCID: PMC10665067.
19. Picciotto S. Regulation of Ghrelin: A Possible Treatment Option for Obesity and Diabetes. Sci J Lander Coll Arts Sci. 2015;8(2):8. Retrieved from https://touroscholar.touro.edu/sjlcas/vol8/iss2/8
20. Özcan B, Delhanty PJD, Huisman M, Visser JA, Neggers SJ, van der Lely AJ. Overweight and obesity in type 1 diabetes is not associated with higher ghrelin concentrations. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2021;13:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-021-00699-4 . PMID: 34294136; PMCID: PMC8296697.
21. Leinonen T, Kesäniemi YA, Hedberg P, Ukkola O. Serum ghrelin and prediction of metabolic parameters in over 20-year follow-up. Peptides. 2016;76:51–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2015.12.002 . Epub 2015 Dec 22. PMID: 26721207.
22. Young ER, Jialal I. Biochemistry, ghrelin. 2019; In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL); 2023. PMID: 31613472.
23. Lv Y, Liang T, Wang G, Li Z. Ghrelin, a gastrointestinal hormone, regulates energy balance and lipid metabolism. Biosci Rep. 2018 Oct;38(5). https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20181061 . PMID: 30177523; PMCID: PMC6153372.
24. Mani BK, Shankar K, Zigman JM. Ghrelin’s Relationship to Blood Glucose. Endocrinology [Internet]. 2019 May 1;160(5):1247–61. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2019-00074
25. Haddawi KH, Al-Ziaydi AG, Al-Kathem Al-Khalidi FA. The role of adipokines and ghrelin in interactions and clinical implications in childhood obesity. J Educ Health Promot. 2024;13:40. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_972_23 . PMID: 38545313; PMCID: PMC10968273.
التنزيلات
منشور
إصدار
القسم
الرخصة
الحقوق الفكرية (c) 2025 Safa A. Ayash, Hedef Dh. Elyaseen, Munib A. Alzubaidi

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


