Imbalance of Pro and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis in Iraqi Patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad.6632419Keywords:
Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Arthritis, Cytokines, Interleukin, RheumatoidAbstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune chronic inflammatory illness that affects the whole body and is characterized by non-articular involvement and inflammatory arthritis. It often develops by an interaction between genes and environmental factors.
Objectives: This research was designed to investigate the effect of the imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines on patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in comparison, with healthy controls.
Methods: Two groups (One"hundred) of patients with Rheumatoid arthritis (66female, 34 male) and 50 healthy control group (28female, 22 male)) were chosen in this study to investigate the effect of some laboratory parameters such as cytokines IL1, IL4, IL6, and IL20 measured by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)on patients visiting health institutions in the Al-Anbar Governorate / Iraq. The results of the laboratory tests of patients who had symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis were compared with the laboratory test results of healthy people for comparison.
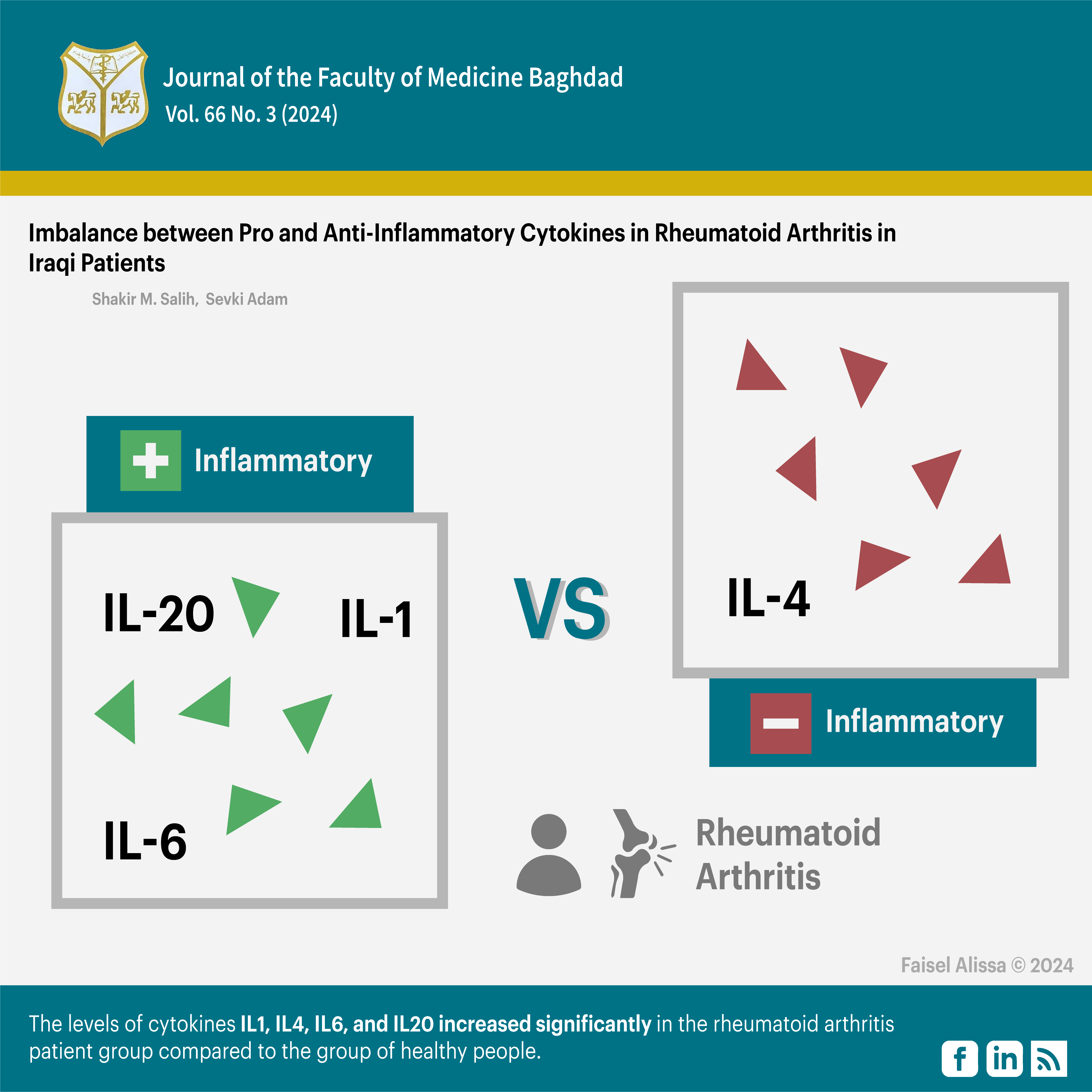
Results: The results indicated that the level of the cytokine IL1 increased significantly in the rheumatoid arthritis patient group (23.24 pg/mL) when compared with the group of healthy people (3.48 pg/mL). The results showed that the level of cytokine IL6 significantly increased in the rheumatoid arthritis patient group (50.66 pg/mL) compared to the healthy group (3.36 pg/mL). The results of cytokine IL20 significantly increased in the rheumatoid arthritis patient group (46.03 pg/mL) compared to the healthy group (15.02 pg/mL). The cytokine IL4 level showed a significant increase within the rheumatoid arthritis patient group (51.95 pg/mL) compared with the healthy people group (9.09 pg/mL).
Conclusion: The levels of cytokines IL1, IL4, IL6, and IL20 increased significantly in the rheumatoid arthritis patient group compared to the group of healthy people.
Received: July 2024
Revised: August, 2024
Accepted: Sept., 2024
Downloads
References
Smolen, J. S., Landewé, R. B., Bergstra, S. A., Kerschbaumer, A., Sepriano, A., Aletaha, D. and Van Der Heijde, D. 2023. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological diseasemodifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 82(1): 3-18. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2022-223356.
Deane, K. D., Demoruelle, M. K., Kelmenson, L. B., Kuhn, K. A., Norris, J. M. and Holers, V. M. 2017. Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Practice and Research Clinical Rheumatology, 31(1): 3-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2017.08.003.
Gravallese, E. M. and Firestein, G. S. 2023. Rheumatoid Arthritis—Common Origins, Divergent Mechanisms. New England Journal of Medicine, 388(6): 529-542. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra2103726.
Kato, E., Sawada, T., Tahara, K., Hayashi, H., Tago, M., Mori, H. and Tohma, S. 2017. The age at onset of rheumatoid arthritis is increasing in Japan: a nationwide database study. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, 20(7): 839-845. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12998.
Yu, F., Chen, H., Li, Q., Tao, M., Jin, Z., Geng, L. and Sun, L. 2023. Secular trend of mortality and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in global, 1990–2019: an age period cohort analysis and joinpoint analysis. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 23(1): 356. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-023-02594-2 .
Bullock, J., Rizvi, S. A., Saleh, A. M., Ahmed, S. S., Do, D. P., Ansari, R. A. and Ahmed, J. 2018. Rheumatoid arthritis: a brief overview of the treatment. Medic Principles and Practice, 27(6): 501-507. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493390.
Oglah, A. A., Mohammed, K. I. A., & Alosami, M. H. 2022. A comparative study of serum amyloid A2 with anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in the prognosis of a group of rheumatoid arthritis patients in Iraq. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine Baghdad, 64(3), 153-158. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.6431947.
Maranini, B., Bortoluzzi, A., Silvagni, E. and Govoni, M. 2022. Focus on sex and gender: what we need to know in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(3): 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030499.
Kovacs, W. J. and Olsen, N. J. 2011. Sexual dimorphism of RA manifestations: genes, hormones and behavior. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 7(5): 307-310. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.231.
Hughes, G. C. and Choubey, D. 2014. Modulation of autoimmune rheumatic diseases by oestrogen and progesterone. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 10(12): 740-751. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2014.144.
Alpizar-Rodriguez, D., Lesker, T. R., Gronow, A., Gilbert, B., Raemy, E., Lamacchia,C. and Strowig, T. 2019. Prevotella copri in individuals at risk for rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 78(5): 590-593. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214514.
Mohammed, A. M., Zayni, S. M., AL-Anee, M. M., Corial, F. I., & Al-Rubaee, A. 2023. Diagnostic and predictive values of IL-6 in a group of Iraqi patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine Baghdad, 65(2). https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.2044.
Abuhelwa, A. Y., Hopkins, A. M., Sorich, M. J., Proudman, S., Foster, D. J. and Wiese, M. D. 2020. Association between obesity and remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Scientific Reports, 10(1): 18634. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-75673-7.
Qin, B., Yang, M., Fu, H., Ma, N., Wei, T., Tang, Q. and Zhong, R. 2015. Body mass index and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Arthritis Research and Therapy, 17: 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-015-0601-x.
Jassim, H. H. M., Alnassiri, S. H. M., Mawlood, A. F. and Shnak, Q. A. 2021. Relationship of erythrocyte sedimentation rate with the activity of prolidase and liver enzyme in serum of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Materials Today: Proceedings, 43: 2069-2075. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATPR.2020.11.845.
Kay, J. and Calabrese, L. 2004. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology, 43(3), iii2-iii9. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh201.
Omran, R. H., Zahra'a, A. A., & Alrawi, A. A. 2022. Evaluation of Some New Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine Baghdad, 64(3), 159-162. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.6431963.
Boraschi, D. 2022. What is IL-1 for? The functions of interleukin-1 across evolution. Frontiers in Immunology, 13: 872155. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.872155.
Santos Savio, A., Machado Diaz, A. C., Chico Capote, A., Miranda Navarro, J., Rodríguez Alvarez, Y., Bringas Pérez, R. and Guillen Nieto, G. E. 2015. Differential expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-15Ralpha, IL-15, IL-6 and TNFalpha in synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 16(1): 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-015-0516-3.
Pandolfi, F., Altamura, S., Frosali, S. and Conti, P. 2016. Key role of DAMP in inflammation, cancer, and tissue repair. Clinical Therapeutics, 38(5): 1017-1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.02.028.
Hsu, Y. H., Li, H. H., Hsieh, M. Y., Liu, M. F., Huang, K. Y., Chin, L. S. and Chang, M. S. 2006. Function of interleukin‐20 as a proinflammatory molecule in rheumatoid and experimental arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 54(9): 2722- 2733. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22039
Kragstrup, T. W., Andersen, M. N., Schiøttz-Christensen, B., Jurik, A. G., Hvid, M. and Deleuran, B. 2017. Increased interleukin (IL)-20 and IL-24 target osteoblasts and synovial monocytes in spondyloarthritis. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 189(3): 342-351. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12973.
Hussien, D. T., Shabana, A. A., Hassan, A. S. and Elmarghany, E. B. 2022. Assessment of serum interleukin-20 level in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Relation to disease activity and ultrasound measures. The Egyptian Rheumatologist, 44(2): 181-186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejr.2022.01.002.
Giri, P. S., Shah, F., Gupta, B., Dhangar, A., Pathak, V. N., Desai, B. and Dwivedi, M. 2021. Genetic association of interleukin-4 VNTR polymorphism with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in South Gujarat population. Gene Reports, 25: 101322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genrep.2021.101322.
Wallis, S. K., Cooney, L. A., Endres, J. L., Lee, M. J., Ryu, J., Somers, E. C. and Fox, D. A. 2011. A polymorphism in the interleukin-4 receptor affects the ability of interleukin-4 to regulate Th17 cells: a possible immunoregulatory mechanism for genetic control of the severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research and Therapy, 13(1): 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3239.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Shakir M. Salih, Sevki A. Adam

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


