The Relationship between Serum Zinc and Glycemic Control among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Khartoum State, Sudan
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad2450Keywords:
Glycemic control, HbA1c, Serum Zinc levels, Type 2 Diabetes, Zinc deficiencyAbstract
Background: Previous studies suggest a significant relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and a lack of zinc. A lack of zinc can negatively impact insulin synthesis, storage, and secretion, leading to insulin resistance and inadequate glycaemic control. Nevertheless, the correlation between serum zinc levels and glycaemic control in T2DM has not been well studied in various populations.
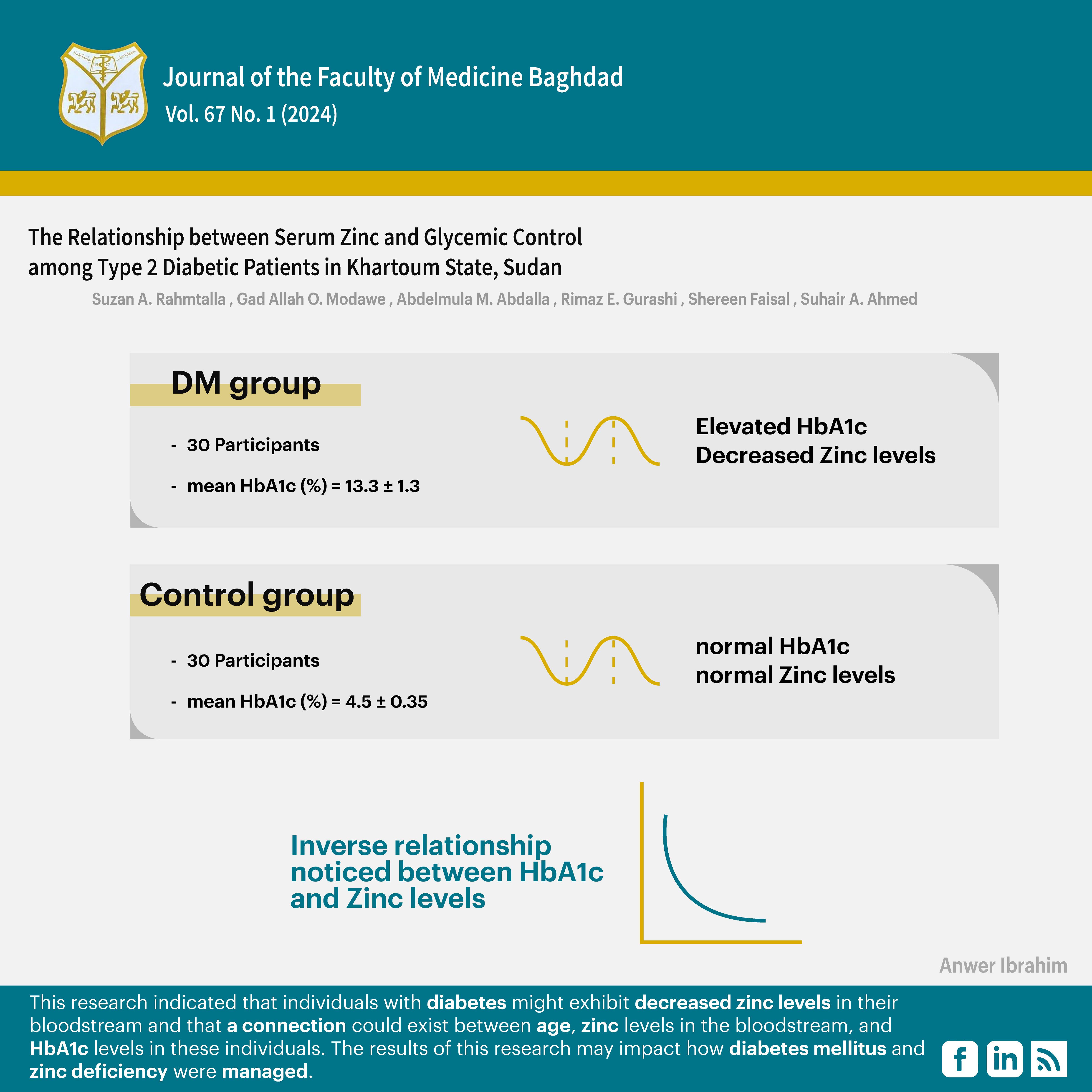
Objective: To investigate the relationship between serum zinc levels and glycaemic control, assessed by HbA1c, in individuals diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: This case-control study was carried out between April 2018 and July 2019 at Omdurman Teaching Hospital in Khartoum State, Sudan. The study included 100 participants: 50 were T2DM patients, and the other 50 were healthy individuals who served as controls. Serum zinc levels were determined with atomic absorption spectrophotometry, while HbA1c levels were evaluated with the Ichroma system. Data analysis was performed using SPSS, version 25. A comparative analysis was conducted on the groups, with correlation coefficients being calculated to investigate the correlations between age, serum zinc, and HbA1c levels.
Results: The diabetics showed notably lower zinc levels in their blood compared to the control group, along with notably elevated HbA1c levels. In diabetic individuals, age correlated positively with HbA1c and serum zinc levels. Additionally, diabetic patients showed a significant inverse correlation between their serum zinc levels and HbA1c values.
Conclusion: This research indicates that individuals with diabetes might exhibit decreased zinc levels in their bloodstream and that a connection could exist between age, zinc levels in the bloodstream, and HbA1c levels in these individuals. The results of this research may impact how diabetes mellitus and zinc deficiency are managed.
Received: Aug., 2024
Revised: Jan., 2025
Accepted: Jan. 2025
Published: April 2025
Downloads
References
1. Aruoah MK, Al-Jowar SA. The effects of zinc and vitamin C supplementation on the glycemic profile in type 2 diabetic patients. Iraqi J Sci. 2022;63(1):70-6. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2022.63.1.8.
2. World Health Organisation. Global report on diabetes. 2016. http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204871/1/9789241565 57_eng.pdf.
3. Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;94(3):311-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2011.10.029.
4. El Dib R, Gameiro OL, Ogata MS, Módolo NS, Braz LG, Jorge EC, et al. Zinc supplementation for the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults with insulin resistance. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021; 2021(2): CD005525. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005525.pub3.
5. Farooq M, Ali F, Alamri B, Alwhahabi B, Metwally AM, Kareem KA. Zinc deficiency in diabetic patients and its relation to hyperglycemia. J Fam Community Med. 2020;27(1):29-33. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_113_19/
6. Farooq M. Zinc deficiency is associated with poor glycemic control. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2019;29(3):253-7. https://doi.org/10.29271/jcpsp.2019.03.253.
7. Hussain SS, Rajendiran KS, Mohan M, Munisammy L, Velu K, Cassinadane AV. Serum zinc and magnesium levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients on metformin therapy. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021;20(2):1-6. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/350808827_Serum_Zinc_and_Magnesium_Levels_in_Type_2_Diabetes_Mellitus_Patients_on_Metformin_Therapy.
8. Tripathy S, Sumathi S, Bhupal RG. Minerals nutritional status of type 2 diabetic subjects. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2021;41(3):476-80. https://rssdi.in/newwebsite/journal/2004_jan-mar/original_article4.pdf.
9. Osman E, Levent K, Nuriye U, Demet A, and Ahmet O. Correlations of serum Cu2+, Zn2+, Mg2+ and HbA1c in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Turk J Endocrinol Metab. 2004;24(1):45-9. https://endocrinolrespract.org/Content/files/sayilar/111/8-2-0_75-79.pdf.
10. Belete V, Dib R, Attah A. Zinc supplements for the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019; 10:CD005525. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD005525.
11. Da Porto A, Miranda C, Brosolo G, Zanette G, Michelli A, Ros RD. Nutritional supplementation on wound healing in diabetic foot: what is known and what is new? World J Diabetes. 2022; 13(11):940-948. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i11.940.
12. Abbas NK, Mohsin AA, Humiash HH, Radhi MM. Estimation of oxidative stress, oxidized LDL and some trace elements in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Al-Nisour J Med Sci. 2022;4(2). https://doi.org/10.70492/2664-0554.1077.
13. Saharia GK, Goswami RK. Evaluation of serum zinc status and glycated hemoglobin of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Assam. J Lab Physicians 2013; 5:30-3. Published: 2020-04-07. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2727.115923.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Suzan A. Rahmtalla, Gad Allah Modawe, Abdelmula M. Abdalla, Rimaz Gurashi, Shereen F. Hamad, Suhair A, Rahmtalla

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


