Histopathological Study of Urinary Bladder Cancer in a Group of Iraqi Patients from 2019 to 2024
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad2444Keywords:
Urinary bladder cancer, Histopathological study, Clinicopathological featuresAbstract
Background: Urinary bladder cancer (UBC) is the most common urinary tract malignancy, ranking tenth worldwide. In Iraq, UBC is ranked as the seventh most prevalent cancer among the top 10 cancers. Numerous established risk factors for bladder cancer including genetic and hereditary factors, smoking and nicotine behaviors, occupational exposure to certain chemicals and pigments, and environmental pollution from drinking water contaminated with arsenic may also be problems, as well as disorders including chronic cystitis, and infectious diseases like schistosomiasis. Urine cytology and cystoscopy are the gold standard for detecting UBC.
Objectives: To analyze and characterize urinary bladder cancer (UBC) diagnosed in a group of Iraqi patients.
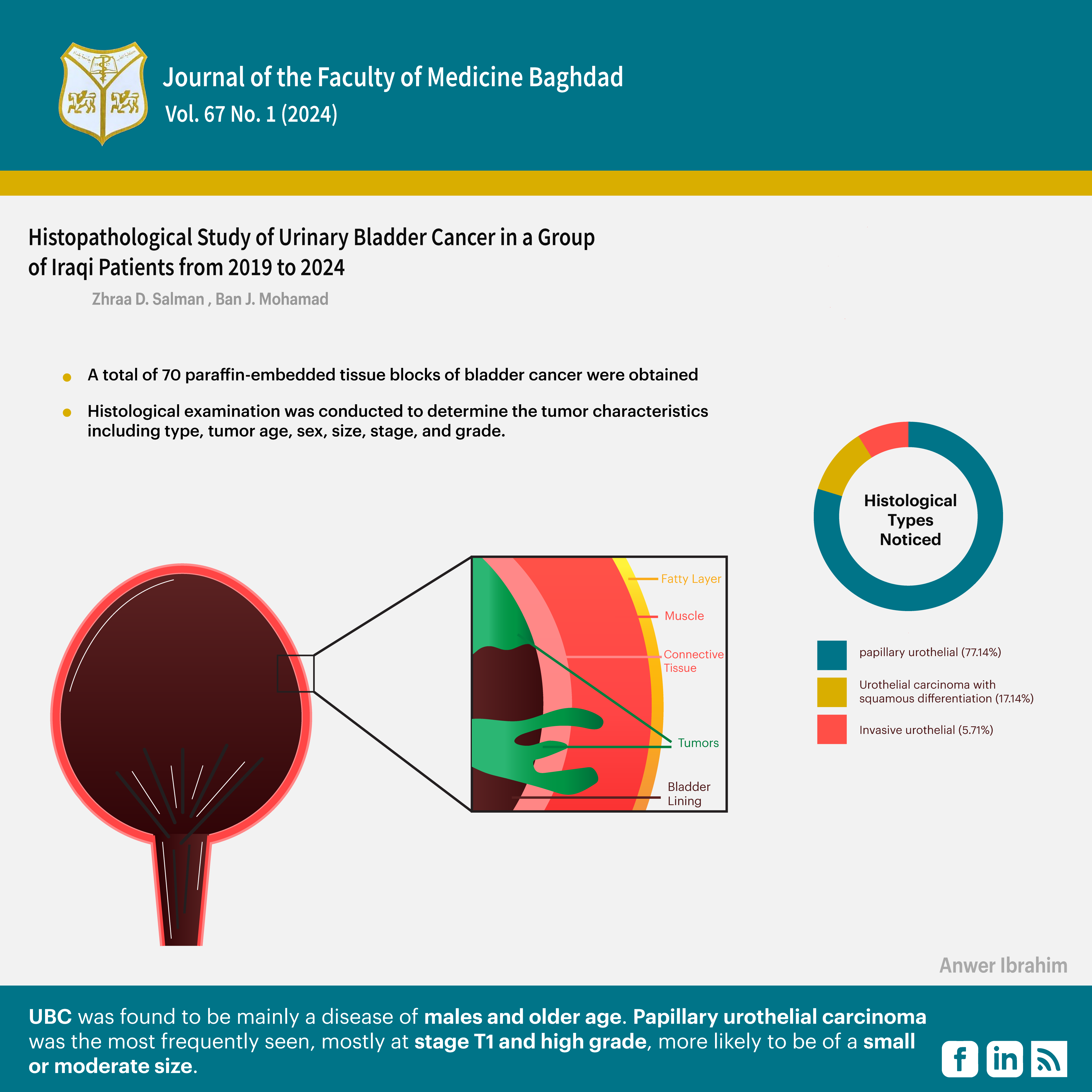
Cases and methods: A total of 70 paraffin-embedded tissue blocks of bladder cancer were obtained from the archive of the Histopathology Unit of the Martyr Ghazi Al-Hariri/ Medical City, Al-Yarmouk Teaching Hospital, and several private laboratories in Baghdad, Iraq for cases diagnosed between 2019 and 2024. Clinical data in addition to the age and sex of the patients were collected from the patients' clinical records. Histological examination was conducted to determine the tumor characteristics including type, tumor age, sex, size, stage, and grade.
Results: The results revealed that 82.9% of UBC cases were males, and 62.9% were between the ages of 60 and 79 years. The most common tumor size was 2-5 cm, with stage T1 accounting for 80% of the total. A high tumor grade was observed in 60% of UBC cases. The most prevalent histological type observed was papillary urothelial carcinoma (77.1%).
Conclusion: UBC was found to be mainly a disease of males and older age. Papillary urothelial carcinoma was the most frequently seen, mostly at stage T1 and high grade, more likely to be of a small or moderate size.
Received: July 2024
Revised: Nov. 2024
Accepted: Dec. 2024
Published April.2025
Downloads
References
1. Zhao J, Li J, Zhang R. Off the fog to find the optimal choice: Research advances in biomarkers for early diagnosis and recurrence monitoring of bladder cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023;1878(4):188926.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188926.
2. Ministry of Health, Iraqi cancer board. Cancer Registry of Iraq Annual Report 2022. Baghdad: Iraqi Cancer Registry Center, Ministry of Health, 2022. https://storage.moh.gov.iq/2024/03/31/2024_03_31_11983087032_3940351786864953.pdf
3. Ibraheem NIA, Ali RH, Ismail MB. Kidney functions and electrolyte disturbance among Iraqi patients with bladder cancer. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine Baghdad. 2022;64(4):214-217.
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.6441985 .
4. Kawada T, Yanagisawa T, Rajwa P, Motlagh RS, Mostafaei H, Quhal F, et al. The prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Genitourinary Cancer. 2024;22(2):535-543.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clgc.2024.01.008.
5. Kang Y, Park C, Lee H, Kang S, Cheon C, Kim B. Natural Products as New Approaches for Treating Bladder Cancer: From Traditional Medicine to Novel Drug Discovery. Pharmac. 2023;15(4):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041117
6. Tabaei S, Haghshenas MR, Ariafar A, Gilany K, Stensballe A, Farjadian S, et al. Comparative proteomics analysis in different stages of urothelial bladder cancer for identification of potential biomarkers: Highlighted role for antioxidant activity. Clin Proteom. 2023;20(1):28.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12014-023-09419-8.
7Al-Humairi R, Ad’hiah A. Systemic interleukin-6 response after intravesical instillation of Bacillus calmette-guérin and mitomycin C in superficial bladder cancer. Arch. Razi Inst. 2023;78(1):353-360.
https://doi.org/10.22092/ARI.2022.358957.2344 .
8. Al-Humairi RM, Al-Musawi MT, Ad’hiah AH. Serum level and single-nucleotide polymorphisms of toll-like receptor-7 among urinary bladder cancer Iraqi patients. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics. 2019 Dec;20:1-9.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43042-019-0015-4
9. Gil D, Zarzycka M, Dulińska-Litewka J, Ciołczyk-Wierzbicka D, Lekka M, Laidler P. Dihydrotestosterone increases the risk of bladder cancer in men. Human Cell. 2019;32:379-389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-019-00255-3
10. Alyasiri MH, Atiyah SAA. Identify the urinary bladder cancer patterns in Nasiriyah City/Thi-qar province–Iraq. Univ Thi-Qar JSci. 2023;10(2):87-91.
https://doi.org/10.32792/utq/utjsci/v10i2.1091.
11. Mohammed MJ, Ahmed BS. Expression of cancer stem cell marker octamer-binding transcription factor 4 in high-grade transitional cell carcinoma. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2019;12(6):1-4.
http://dx.doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2019.v12i6.33189.
12. Ragab HH, El-Badry MSM, Abdel Ghani MM, Aboelhassan MHM. Urinary bladder carcinoma pattern at Urology Minia University Hospital. MJMR. 2021;32(1):36-43.
https://mjmr.journals.ekb.eg/article_220576_e2c35c435a138fadcf0b7b1c363ce1b6.pdf
13. Gupta R, Khan SM, Mahajan M, Sharma P, Mahajan A. Urinary bladder carcinoma in females: A clinico-pathological assessment. Cureus. 2023;15(5): e39753. https://doi.org/10.7759%2Fcureus.39753.
14. Hussein YF. Regional differences in histological features of bladder cancer diagnosed in post-war Iraq. Int J Cancer Epid & Res. 2017;1(2):28-33.
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Jalal Jalal/publication/337622418_Regional_Differences_in_Histological_Features_of_Bladder_Cancer_Diagnosed_in_Post-War_Iraq/data/5de0d278a6fdcc2837f3ee8a/18f8b88ae14e4e70b8b834fbd4993cf7538e.pdf
15. Rashidian H, Zendehdel K, Daroudi R, Ebadzadeh MR, Haghdoost AA. Epidemiology and hospitalization cost of bladder cancer in Kerman Province, Southeastern Iran. Iran. J. Public Health. 2018;47(4):567-574.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5996338/
16. Yohana C, Bakuza JS, Kinung’hi SM, Nyundo BA, Rambau PF. The trend of schistosomiasis related bladder cancer in the lake zone, Tanzania: A retrospective review over 10 years period. Infec Ag and Canc. 2023;18(1):10.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13027-023-00491-1.
17. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019;69(1):7-34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551.
18. Rambau PF, Chalya PL, Jackson K. Schistosomiasis and urinary bladder cancer in North Western Tanzania: a retrospective review of 185 patients. Infectious agents and cancer. 2013; 8:1-6.
https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-9378-8-19.
19. Kamal NN, Mahmoud AMEA, Khalifa MAZ, Mohammed KH, Hassan EE. Association between smoking and urinary bladder cancer (BC): case control study in Minia, Egypt. Minia Journal of Medical Research. 2023;34(1):279-288.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/mjmr.2023.181521.1246
20. Teoh JY-C, Huang J, Ko WY-K, Lok V, Choi P, Ng C-F, et al. Global trends of bladder cancer incidence and mortality, and their associations with tobacco use and gross domestic product per capita. Eur. Urol. 2020;78(6):893-906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.09.006.
21. Nagata Y, Miyamoto H. The prognostic role of steroid hormone receptor signaling pathways in urothelial carcinoma. Translational Cancer Research. 2020;9(10):6596–6608. https://doi.org/10.21037%2Ftcr.2020.01.06.
22. Mohammed AS, Ali HH, Qasim BJ, Chaloob MK. CD10 and CA19. 9 immunohistochemical expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Urol. Ann. 2013;5(2):81-85. DOI: 10.4103/0974-7796.110002.
23. Moussa S, El-Sheshtawy W. Pathological pattern of urinary bladder cancer: Data from a single Egyptian institute. Res Oncol. 2017;13(1):14-17.
https://dx.doi.org/10.21608/resoncol.2017.869.1023.
24. Diana P, Lughezzani G, Saita A, Uleri A, Frego N, Contieri R, et al. Head-to-head comparison between high-resolution microultrasound imaging and multiparametric MRI in detecting and local staging of bladder cancer: The bus-miss protocol. Bladder Cancer. 2022;8(2):119-127.
https://doi.org/10.3233/BLC-211611.
25. Abdel-Rahman HM, El Fiki IM, Desoky EA, Elsayed ER, Abd Samad KM. The role of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in T staging and grading of urinary bladder cancer. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2015;46(3):741-747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrnm.2015.03.006.
26. Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L. Stage T1 bladder cancer: Diagnostic criteria and pitfalls. Pathol. 2021;53(1):67-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathol.2020.09.014.
27. Al-Maghrabi J. CD10 expression in urinary bladder urothelial carcinoma is associated with high-tumor grade and stage. Pak J Med Sci. 2023;39(1):192 –197. https://doi.org/10.12669%2Fpjms.39.1.6268.
28. Abdelrahman AE, Rashed HE, Elkady E, Elsebai EA, El-Azony A, Matar I. Fatty acid synthase, Her2/neu, and E2F1 as prognostic markers of progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2019; 39:42-52.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2019.01.002
29. Wang S, Ji Y, Liu Y, Du P, Ma J, Yang X, et al. The values of HER-2 expression in the non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: a retrospective clinical study. Frontiers in Oncology. 2023;13:1243118.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1243118.
30. Mariappan P, Johnston A, Padovani L, Clark E, Trail M, Hamid S, et al. Enhanced quality and effectiveness of transurethral resection of bladder tumour in non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A multicentre real-world experience from Scotland’s quality performance indicators programme. Eur. Urol. 2020;78(4):520-530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.06.051.
31. Abbas SM, Dhahi MAR, Muhammad SH. Evaluation of gene expression level of miRNA-29c, miRNA-125, miRNA-141, miRNA-145 and miRNA-205 as predisposing factors for transitional cell carcinoma-bladder cancer in Iraqi patients. Iraqi J. Sci. 2023;64(8):3799-3811. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2023.64.8.7.
32. Al-Saraireh YM, Alshammari FO, Youssef AM, Al-Sarayreh S, Almuhaisen GH, Alnawaiseh N, et al. Profiling of CYP4Z1 and CYP1B1 expression in bladder cancers. Sci. Rep. 2021;11(1):5581.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85188-4.
33. Yazdi SAM, Asghari F, Tabriz HM, Vesali B, Nazar E. The value of epidermal growth factor receptor expression in predicting aggressive behaviors of bladder neoplasms. Nephro-Urol. Mon. 2023;15(2):e137778. https://doi.org/10.5812/numonthly-137778.
34. Ibrahim ZI, Hussein AG, Qasim BJ. Histopathological evaluation of papillary urothelial lesions of the urinary bladder in a sample of Iraqi patients. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research.2022;11(4):1-16.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Zhraa D. Salman, Ban J. Mohamad

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


