Study of Adhesion Molecules in Diabetes Mellitus Type2 Iraqi Patients with Dyslipidemia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.6622273Keywords:
Diabetes mellitus; , Dyslipidemia;, VCAM-1;, ICAM-1Abstract
Background: Cell adhesion molecules are protein entities that are located on the cell surface. The vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) expression is related to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with dyslipidemia.
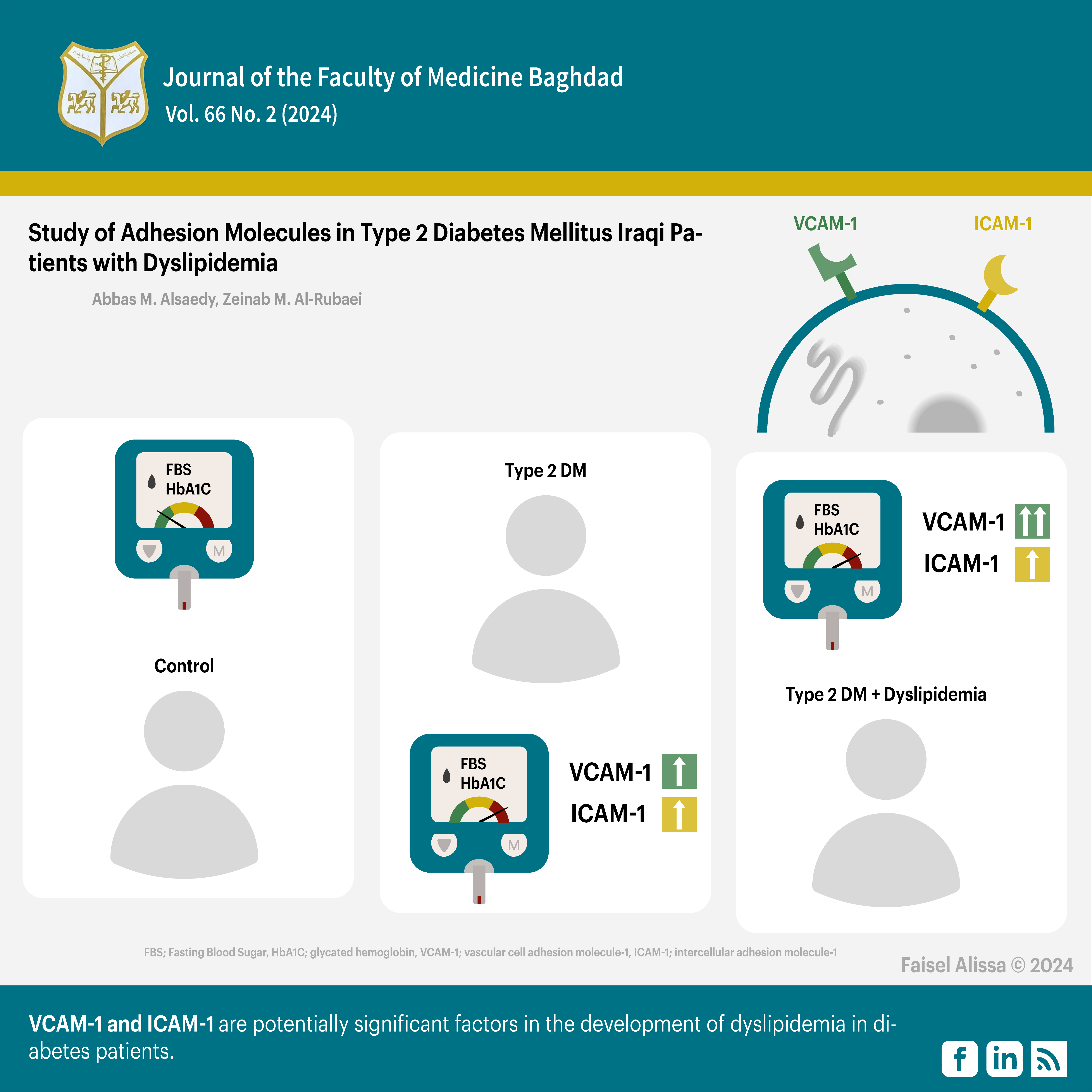
Objectives: To determine the levels of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 in T2DM patients with dyslipidemia and to explore the relationship between VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 and the development of dyslipidemia in T2DM patients.
Patients and methods: The study included 150 individuals with an age range of (35-55) years. Patients with diabetes for more than 5 years were excluded. Fifty healthy individuals constituted Group 1 (G1), fifty patients with T2DM constituted Group 2 (G2), and fifty T2DM patients with dyslipidemia constituted Group 3 (G3). Whole blood samples were drawn to measure HbA1c based on fluorescence immunoassay technology. The serum was separated to measure fasting blood glucose (FBG), triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL) by manual methods, while VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 were determined using the ELISA test. The study was conducted between November 2022 and April 2023 at the National Center for Diabetes Treatment and Research, Baghdad, Iraq.
Results: Significantly higher levels of FSG and HbA1c were detected in G2 and G3 compared to G1, but non-significantly so when G3 was compared to G2. Significant higher levels of TG and TC levels were detected for G3 when compared to G1 and G2, but non-significantly so when G2 was compared to G1. HDL levels were significantly lower in G3 compared to G2 and G1, but non-significantly so when G2 was compared to G1. VCAM-1, and ICAM-1 were significantly higher in G2 compared to G1, and VCAM-1 level was significantly higher in G3 compared to G2. Non-significant differences in ICAM-1 levels were found between G3 and G2.
Conclusion: VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 are potentially significant factors in the development of dyslipidemia in diabetes patients. They might serve as biomarkers to accurately predict the progression of cardiovascular disease.
Downloads
References
- Jialal I, Singh G. Management of diabetic dyslipidemia: An update. World journal of diabetes. 2019 May 5;10(5):280. https://doi.org/10.4239%2Fwjd.v10.i5.280
- Ahmed HS, Mohammed MS. Atherogenic Indices in Type 2 Diabetic Iraqi Patients and Its Association with Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine Baghdad. 2023 Oct 1;65(3):179-86. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.2075 .
- Al-Ghurabi ME, Muhi AA, Al-Mudhafar DH. Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 as markers of atherosclerosis of NIDDM. Am J Life Sci. 2015;3(1):22-6.
https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajls.20150301.15 .
- Hegazy GA, Awan Z, Hashem E, Al-Ama N, Abunaji AB. Levels of soluble cell adhesion molecules in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with macrovascular complications. Journal of International Medical Research. 2020 Oct;48(4):0300060519893858. DOI: 10.1177/0300060519893858 .
- Palella E, Cimino R, Pullano SA, Fiorillo AS, Gulletta E, Brunetti A, et al. Laboratory parameters of hemostasis, adhesion molecules, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: correlation with glycemic control. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020 Jan;17(1):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17010300
- Müller N. The role of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in the pathogenesis of psychiatric disorders. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2019 Nov 22;10:1251. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01251. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01251 .
- Bui TM, Wiesolek HL, Sumagin R. ICAM-1: A master regulator of cellular responses in inflammation, injury resolution, and tumorigenesis. Journal of Leucocyte Biology. 2020 Sep;108(3):787-99. https://doi.org/10.1002/JLB.2MR0220-549
- Bereda G. Pathophysiology and Management of Dyslipidaemia. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res. 2022;43(2). https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2022.43.006869 .
- Hasheminasabgorji E, Jha JC. Dyslipidemia, diabetes, and atherosclerosis: role of inflammation and ROS-redox-sensitive factors. Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 3;9(11):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111602 .
- Blum A, Pastukh N, Socea D, Jabaly H. Levels of adhesion molecules in peripheral blood correlate with stages of diabetic retinopathy and may serve as biomarkers for microvascular complications. Cytokine. 2018 Jun 1;106:76-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2017.10.014 .
- Alfarisi HA, Ibrahim M, Mohamed ZB, Hamdan AH, Mohamad CC. Trihoney suppresses soluble adhesion molecules (ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) in hypercholesterolemic atherosclerotic rabbits: a comparative study with atorvastatin. Sains Malaysiana. 2020 Jun 1;49(6):1313-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2020-4906-09 .
- Al-Rubaei ZM, Abdulhadi GH, Alrubaye IM, Alrugaibi AH. Comparative study of fetuin-a levels l Iraqi diabetic patients with hyper and thyroid disorder. Biochemical and Cellular Archives. 2021 Apr 1;21(1):53-7. https://connectjournals.com/03896.2021.21.53 .
- Abass EA, Abed BA, Mohsin SN. Study of lysyl oxidase-1 and kidney function in sera of Iraqi patients with diabetic nephropathy. Biochemical & Cellular Archives. 2021 Apr 1;21(1). https://connectjournals.com/03896.2021.21.1129.
- Jafer AA, Ali BH. Relationship between cathepsin K and total oxidative state in diabetes mellitus female patients with osteoporosis in Iraq. Biomedicine. 2023 May 4;43(02):621-4. https://doi.org/10.51248/.v43i02.2680.
- Oguntibeju OO. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress, and inflammation: examining the links. International journal of physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. 2019;11(3):45.
www.ijppp.org /ISSN:1944-8171/IJPPP0091641
- Hami AM, DM F. Association between HbA1c and Serum Lipid Profile among a sample of Iraqi Patients with Type2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of the Faculty of Medicine. 2021;63(3). https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.6331864.
- Hasan SM, Al-Rubaei ZM. G-Protein Coupled Receptor Purification from Whole Blood of Iraqi Diabetic and Diabetic Nephropathy Patients. Indian Journal of Public Health Research & Development. 2019 Nov 1;10(11). https://doi.org/10.5958/0976-5506.2019.03918.4
- Hirano T. Pathophysiology of diabetic dyslipidemia. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. 2018 Sep 1;25(9):771-82. http://doi.org/10.5551/jat.RV17023 .
- Jaid HK, Khaleel FM, Salman IN, Abd BA. Estimation of Apelin Levels in Iraqi Patients with Type II Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Baghdad Science Journal. 2023. https://dx.doi.org/10.21123/bsj.2023.ID .
- Bekele S, Yohannes T, Mohammed AE. Dyslipidemia and associated factors among diabetic patients attending Durame General Hospital in Southern Nations, Nationalities, and People’s Region. Diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity: targets and therapy. 2017 Jun 22:265-71. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S135064 .
- Abed BA, Hamid GS. Evaluation of Lipocalin-2 and Vaspin Levels in Iraqi Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Iraqi Journal of Science. 2022 Nov 30:4650-8. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2022.63.11.3 .
- Hameed EK, Al-Ameri LT, Hasan HS, Abdulqahar ZH. The Cut-off Values of Triglycerides-Glucose Index for Metabolic Syndrome Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Baghdad Science Journal. 2022 Apr 1;19(2):0340-. http://dx.doi.org/10.21123/bsj.2022.19.2.0340 .
- Wen J, Huang Y, Lu Y, Yuan H. Associations of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides and the total cholesterol/HDL-c ratio with arterial stiffness independent of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in a Chinese population. Hypertension research. 2019 Aug;42(8):1223-30. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-019-0251-5.
- Albadr A, Haddad NS. Pancreatic Stone Protein/regenerating Protein (PSP/reg) as a Biochemical Marker for Prediction of Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. AL-Kindy College Medical Journal. 2023 Aug 30;19(2):196-201. https://doi.org/10.47723/kcmj.v19i2.966 .
- Jia C, Anderson JL, Gruppen EG, Lei Y, Bakker SJ, Dullaart RP, et al. High-density lipoprotein anti-inflammatory capacity and incident cardiovascular events. Circulation. 2021 May 18;143(20):1935-45. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.050808
- Kunutsor SK, Bakker SJ, Dullaart RP. Soluble vascular cell adhesion molecules may be protective of future cardiovascular disease risk: findings from the PREVENT prospective cohort study. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. 2017 Aug 1;24(8):804-18. http://doi.org/10.5551/jat.38836 .
- Wei Z, Jiang W, Wang H, Li H, Tang B, Liu B, et al. The IL-6/STAT3 pathway regulates adhesion molecules and cytoskeleton of endothelial cells in thromboangiitis obliterans. Cellular signaling. 2018 Apr 1;44:118-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.01.015.
-Abdullah RA, Abdulrahman IS. Circulating Cell Adhesion Molecules Level in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Correlation with Glycemic Control and Metabolic Syndrome: A Case-control Study. Medical Journal of Babylon. 2023 Jan;20(1):64-70.-. https://doi.org/10.4103/MJBL.MJBL_246_22 .
- Hocaoglu-Emre FS, Saribal D, Yenmis G, Guvenen G. Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, and a cluster of differentiation 146 levels in patients with Type 2 diabetes with complications. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2017 Mar 1;32(1):99-105. https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.99 .
- Hegazy GA, Awan Z, Hashem E, Al-Ama N, Abunaji AB. Levels of soluble cell adhesion molecules in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with macrovascular complications. Journal of International Medical Research. 2020 Oct;48(4):0300060519893858. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060519893858.
- Qiu S, Cai X, Liu J, Yang B, Zügel M, Steinacker JM, et al. Association between circulating cell adhesion molecules and risk of type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. 2019 Aug 1;287:147-54. https://doi.org/:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.06.908
- Abbas ZA, El-Yassin HD. The impact of glycemic control on procalcitonin level in patients with type II diabetes. Medical Journal of Babylon. 2022 Jul 1;19(3):391-5. https://doi.org/10.4103/MJBL.MJBL_50_22 .
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Abbas M. Alsaedy, Zeinab M. Al-Rubaei

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


