Exploring the Link between Iron Status and Catalase Activity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad.6632302Keywords:
Catalase activity, Ferritin, Iron, Transferrin, Type 2 DiabetesAbstract
Background: Catalase is an antioxidant enzyme found in all living organisms that is responsible for the degradation of hydrogen peroxide, a type of harmful compound known as reactive oxygen species (ROS), into harmless oxygen and water. It is necessary for cell protection from ROS-induced oxidative damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) individuals. T2DM is rapidly rising in prevalence worldwide, emerging as a significant public health challenge. It can disrupt iron regulation in the bloodstream, leading to the production of ROS, which can damage the cells.
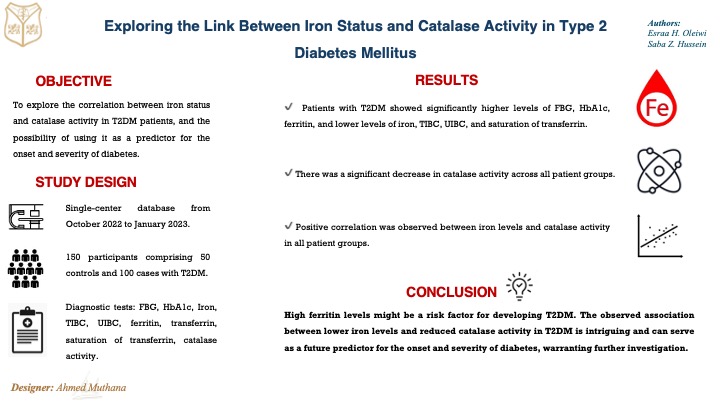
Objective: To explore the correlation between iron status and catalase activity in T2DM patients, and the possibility of using it as a predictor for the onset and severity of diabetes.
Methods: One hundred and fifty participants were included in the study, comprising 50 healthy volunteers who served as the control group (C) and 100 cases diagnosed with T2DM who were divided into three groups based on the duration of their disease: Group A1 (n=38; < 5 years), A2 (n=37; 5-10 years) and A3 (n=25; >10 years). The participants were recruited from the Al-Kindi Teaching Hospital, Baghdad, during the period from October 2022 to the end of January 2023. The study assessed various blood markers in all participants, including Fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), Iron, total iron binding capacity (TIBC), unsaturated iron binding capacity (UIBC), ferritin, transferrin, a saturation of transferrin (S.Trans) and catalase activity (CAT).
Results: Compared to the control group, patients with T2DM showed significantly higher levels of FBG, HbA1c, and ferritin, notably lower levels of iron, TIBC, UIBC, and S.Trans. Interestingly, only the A2 group had significantly lower transferrin levels compared to control. There was a significant decrease in catalase activity across all patient groups. Additionally, a positive correlation was observed between iron levels and catalase activity in all patient groups.
Conclusion: Increases in ferritin levels might be a risk factor for developing T2DM. The observed association between lower iron levels and reduced catalase activity in T2DM is intriguing and can serve as a future predictor for the onset and severity of diabetes, warranting further investigation.
Received: Feb. 2024
Revised: June. 2024
Accepted: July. 2024
Downloads
References
Kim JD, Lim DM, Park KY, Park SE, Rhee EJ, Park CY, et al. Serum Transferrin Predicts New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study. Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2020;35:610-617. https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.721.
Galaris D, Barbouti A, Pantopoulos K. Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: An intimate relationship. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research. 2019;1866(12):118535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118535.
Elsayed ME, Sharif MU, Stack AG. Transferrin Saturation: A Body Iron Biomarker. Advances in Clinical Chemistry. 2016;75:71-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2016.03.002.
Saed HHM, Ali ZA. Correlation and comparison of some trace elements and their related proteins in Type 2 Diabetes mellitus in Kalars city/Kurdistan-Iraq. Al-Qadisiyah Journal of Pure Science. 2022;27(1):17-31. https://doi.org/10.29350/jops.2022.27.2.1493.
Fillebeen C, Lam NH, Chow S, Botta A, Sweeney G, Pantopoulos K. Regulatory Connections between Iron and Glucose Metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207773.
Arumugam S, Suyambulingam A. Association between Serum Ferritin and the Duration of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Chennai. Cureus.2024;16(1): e53117. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.53117.
Liu J, Li Q, Yang Y, Ma L. Iron metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Journal of Diabetes Investigation. 2020;11: 946–955. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13216.
Kuba RH, Saheb EJ, Mosa IS. Detection of Iron and Ferritin in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Patients. Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences. 2022;18(Supp 4):7-10. https://medic.upm.edu.my/upload/dokumen/202203151721452_0149.pdf.
Hamed AME, El Hadidy KE, Salem MN. Ferritin as a marker of Insulin Resistance in Diabetic Patients.Egyptian Journal of Medical Research (EJMR). 2022;3(2):110-120. https://doi.org/10.21608/EJMR.2022.237765.
Hasankhani MB, Mirzaei H, Karamoozian A. Global trend analysis of diabetes mellitus incidence, mortality, and mortality-to-incidence ratio from 1990 to 2019. Scientific Reports. 2023; 13: 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-49249-0.
Dilworth L, Facey A, Omoruyi F. Diabetes Mellitus and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipose Tissues. International Journal Molecular Sciences. 2021;22(14):1-18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147644.
AL-Mohammad HMK, Jawad MM, Ali HA, Hassan F. Role Iron in Diabetes mellitus type 2 patients in province Diwaniya. Al-Kindy College Medical Journal. 2017;13(1):63-65. https://doi.org/10.47723/kcmj.v13i1.125.
Demir S, Nawroth PP, Herzig S, Ekim Üstünel B. Emerging Targets in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(18):1-23. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202100275.
Abusaib M, Ahmed M, Nwayyir HA, Alidrisi HA, Al-Abbood M, Al-Bayati A, et al. Iraqi Experts Consensus on the Management of Type 2 Diabetes/Prediabetes in Adults. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes. 2020;13:1-11. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179551420942232.
Abuyassin B, Laher I. Diabetes epidemic sweeping the Arab world. World Journal of Diabetes. 2016; 7(8):165. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v7.i8.165.
Al-Attaby AKT, Al-Lami MQD. Role of calcium-regulating hormones, adipocytokines and renal function test in progressing type 2 diabetes mellitus in a sample of Iraqi patients. Iraqi Journal of Agricultural Sciences. 2019; 50(1): 343-351. https://doi.org/10.36103/ijas.v50i1.300.
Mahmood AR. Estimation of oxidative stress and some trace elements in Iraqi men patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Iraqi Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2016;25(1):17-22. https://doi.org/10.31351/vol25iss1pp17-22.
Blesia V, Patel VB, Al-Obaidi H, Renshaw D, Zariwala MG. Excessive Iron Induces Oxidative Stress Promoting Cellular Perturbations and Insulin Secretory Dysfunction in MIN6 Beta Cells. Cells. 2021;10(5):1-20. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051141.
Miao R, Fang X, Zhang Y, Wei J, Zhang Y, Tian J. Iron metabolism and ferroptosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus and complications: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death & Disease. 2023;14(3):1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05708-0.
Harrison AV, Lorenzo FR, McClain DA. Iron and the Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Annual Review of Physiology. 2023; 85:339-362. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-022522-102832.
Malghooth HD, Tahmasebi P, Hamzah NA. Catalase gene Polymorphisims of type 2 Diabetes Patients in Al-Diwaniyah Province, Iraq. Biochemical and Cellular Archives. 2021; 21(2):3429-3434. https://doi.org/connectjournals.com/03896.2021.21.3429.
Angelovski M, Spirovska M, Nikodinovski A, Stamatoski A, Atanasov D, Mladenov M. et al. Serum Redox Markers in Uncomplicated type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Accompanies with Abnormal Iron Levels. Central European Journal for Public Health. 2023;31(2): 133-139. https://doi.org/10.21101/cejph.a7399.
Imam MU, Zhang S, Ma J, Wang H, Wang F. Antioxidants Mediate both Iron Homeostasis and Oxidative Stress. Nutrients. 2017;9(7):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9070671.
Manikandan A, Ganesh M, Silambanan S. Study of Iron Status in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Research. 2015;2(2):77-82. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:76494397.
Eddaikra A, Eddaikra N. Endogenous Enzymatic Antioxidant Defense and Pathologies. Antioxidants - Benefits, Sources, Mechanisms of Action. IntechOpen. 2021. http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.95504.
Junsi M, Takahashi Yupanqui C, Usawakesmanee W, Slusarenko A, Siripongvutikorn S. Thunbergia laurifolia Leaf Extract Increased Levels of Antioxidant Enzymes and Protected Human Cell-Lines In Vitro Against Cadmium. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(1):1-17. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9010047.
Krishna H, Avinash K, Shivakumar A, Al-Tayar NGS, Shrestha AK. A quantitative method for detecting and validating catalase activity at physiological concentration in human serum, plasma and erythrocytes. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021;251:119358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119358.
Abd Al-Hameed NM, Al-Ani AW. Assessment of systemic oxidative stress and antioxidants in Iraqi women with newly diagnosed and tamoxifen-treated breast cancer. Eurasian Chemical Communication. 2023; 5:204-215. https://doi.org/10.22034/ecc.2023.365482.1538.
Lu Z, Lightcap IV, Tennyson AG. An organometallic catalase mimic with exceptional activity, H2O2 stability, and catalase/peroxidase selectivity. Dalton Trans. 2021; 50:15493-15501. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1DT02002A.
Hasan HR, Mahmoud HQ. Iron and its related parameters in serum and saliva of Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic and alcoholic liver disease. MOJ Addiction Medicine & Therapy. 2018;5(6):249-253. https://doi.org/10.15406/mojamt.2018.05.00133.
Yakoviichuk A, Krivova Z, Maltseva S, Kochubey A, Kulikovskiy M, Yevhen Maltsev. Antioxidant Status and Biotechnological Potential of New Vischeria vischeri (Eustigmatophyceae) Soil Strains in Enrichment Cultures. Antioxidants. 2023;12(3):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030654.
Tummalacharla SC, Pavuluri P, Maram SR, Vadakedath S, Kondu D, Karpay S, et al. Serum Activities of Ferritin Among Controlled and Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Cureus. 2022;14(5):e25155. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.25155.
Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2019;157:107843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.
Diwan AG, Vora A, AVaidya N, Padwal MK, Momin AA. Hyperferritinemia: An Early Predictor of Insulin Resistance and Other Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical Journal. 2022; 2(1):20-28. https://doi.org/10.56136/BVMJ/2022_00031.
Al-Musawi HS, Al-Lami MQ, Al-Saadi AH. Assessment of Glycemic Control, Renal Function, and Oxidative Stress Parameters in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Iraqi Journal of Science. 2021;62(12):4628-4638. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2021.62.12.4.
Hussein MK, Saifalla PH. Estimating insulin resistance and creatine kinase among Iraqi patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eurasian Chemical Communication. 2022; 4:1193-1200. https://doi.org/10.22034/ecc.2022.343053.1470.
Alwan MH, Hussein SZ. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress in Iraqi Male Patients with Myocardial Infarction and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Iraqi Journal of Science. 2023;64(10): 4918-4929. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2023.64.10.3.
Al-Attaby AKT, Al-Lami MQD. Effects of Duration and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Diabetic Related Parameters, Adipocytokines and Calcium Regulating Hormones. Iraqi Journal of Science. 2019;60(11),2335-2361. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2019.60.11.5.
Wang J, Zhang L, Bai Y, Wang X, Wang W, Li J, et al. The influence of shorter red blood cell lifespan on the rate of HbA1c target achieved in type 2 diabetes patients with an HbA1c detection value lower than 7. Journal of Diabetes. 2023;15(1):7-14. https://doi.org/10.1111/1753-0407.13345
Bharti R. Long duration of diabetes is associated with inadequate glycemic control and lipid profile. Journal of Research in Applied and Basic Medical Sciences. 2023;9(4):210-214. https://doi.org/10.61186/rabms.9.4.210.
Ito H, Omoto T, Abe M, Matsumoto S, Shinozaki M, Nishio S, et al. Relationships between the duration of illness and the current status of diabetes in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Geriatrics & Gerontology International. 2017;17(1):24-30. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.12654.
Zhu HT, Yu M, Hu H, He QF, Pan J, Hu RY. Factors associated with glycemic control in community-dwelling elderly individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Zhejiang, China: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019; 57:1-11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-019-0384-1.
Davidson MB. Historical review of prediabetes/intermediate hyperglycemia diagnosis: Case for the international criteria. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. 2022;185:109219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2022.109219.
Hizomi AR, Fakhri F, Naeimi TM, Talebi F, Talebi Z, Rashidi N, et al. Prevalence of anaemia and its associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a referral diabetic clinic in the north of Iran. BMC Endocrine Disorders. 2023;23(1):1-8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-023-01306-5.
Liu J, Li Q, Yang Y, Ma L. Iron metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Journal of Diabetes Investigation. 2020;11(4):946-955. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13216.
Ahmed SYA, Albayaty NK. A Study of Hepcidin Levels and Other Biochemical Parameters in Women with Osteoporosis with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Ibn AL-Haitham Journal for Pure and Applied Sciences. 2022;35(4):183–193. https://doi.org/10.30526/35.4.2867.
Hernández C, Lecube A, Carrera A, Simó R. Soluble transferrin receptors and ferritin in Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetic Medicine. 2005;22(1):97-101. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01331.x.
Mohammed KJ, Rubat SK, Imran AF. Association of Iron Profile with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Bio-Medical Science. 2024;4(3):199-205. https://doi.org/10.47191/ijpbms/v4-i3-13.
Taderegew MM, Gebremariam T, Tareke AA, Woldeamanuel GG. Anemia and Its Associated Factors among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Attending Debre Berhan Referral Hospital, North-East Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Blood Medicine. 2020;11:47-58. https://doi.org/10.2147/JBM.S243234.
Shobha MV, Jagadamba A, Prabhakar K, Shashidhar KN. Association of Serum Iron Indices with Insulin Resistance Index in Euglycaemic Offspring’s of Diabetic and Non Diabetic Parents: A Case-control Study. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 2022; 16(7): CC05-CC09. https://doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2022/55678.16593.
Zerin N, Sultana S, Afroz F, Rahman M, Chowdhury SA. Iron Status in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Tertiary Care Hospital Study. Acta Scientific Medical Sciences. 2023;7(9):120-129. https://doi.org/10.31080/ASMS.2023.07.1664.
Saha S, Sarker A, Afrin S, Al-Aharama, Begum IA, Sarker CR, et al. Serum Iron Profile in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Rangpur Medical College. 2023;8(2):40-43. https://doi.org/10.3329/jrpmc.v8i2.69372.
Valenti L, Corradini E, Adams LA, Aigner E, Alqahtani S, Arrese M, et al. Consensus Statement on the definition and classification of metabolic hyperferritinaemia. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2023; 19: 299-310. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-023-00807-6.
Chaudhari RK, Niraula A, Gelal B, Baranwal JK, Sarraf DP, Maskey R. Increased Serum Feffitin Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Hospital Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Universal College of Medical Sciences. 2021;09(02):56-60. https://doi.org/10.3126/jucms.v9i02.42009.
Moirangthem MM, Rajkumari VD. Study of Serum Ferritin and HbA1c Levels in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Evidence-Based Medicine and Healthcare. 2020; 7(27):1282-1285. https://doi.org/10.18410/jebmh/2020/272.
Thilipkumar G, Saravanan A, Ramachandran C, Ashok JN. Mean blood glucose level and glycated haemoglobin level in patients of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus and its correlation with serum ferritin level. International Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011;4(1&2):13-17. http://researchjournal.co.in/upload/assignments/4_13-17.pdf.
Saha S, Sarker A, Afrin S, Al- Aharama, Begum IA, Sarker CR, et al. Serum Iron Profile in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Rangamati Medical College. 2023;8(2):40-43. https://doi.org/10.3329/jrpmc.v8i2.69372.
Mamatha BV, Leela P, Samalad VMS, Rakshitha MN. Effects of Iron on blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus – A study in tertiary care centre. Journal of Cardiovascular Disease Research. 2022;13(04):6-11. https://jcdronline.org/admin/Uploads/Files/62577fb435b147.72470334.pdf.
AL-Adhami IAA, Al-Shamahy HA, Al-Meeril AM. Plasma Ferritin and Hepcidin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Universal Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2019;4(1):1-6. https://doi.org/10.22270/ujpr.v4i1.231.
Memon S, Das B, Nisa N, Anjum S, Rafique S, Memon R. Influence of serum ferritin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The Professional Medical Journal. 2024;31(2):183-188. https://doi.org/10.29309/TPMJ/2024.31.02.7869.
Fillebeen C, Lam NH, Chow S, Botta A, Sweeney G, Pantopoulos K. Regulatory Connections between Iron and Glucose Metabolism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020;21(20):7773. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207773.
Szklarz M, Gontarz-Nowak K, Matuszewski W, Bandurska-Stankiewicz E. Ferrocrinology-Iron Is an Important Factor Involved in Gluco- and Lipocrinology. Nutrients. 2022;14(21):1-22. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14214693.
Zhao L, Zou Y, Zhang J, Zhang R, Ren H, Li L, et al. Serum transferrin predicts end-stage Renal Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients. International Journal of Medical Sciences. 2020;17(14):2113-2124. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.46259.
Arija V, Fernández-Cao JC, Basora J, Bulló M, Aranda N, Estruch R, et al. Excess body iron and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a nested case-control in the PREDIMED (Prevention with Mediterranean Diet) study. The British Journal of Nutrition. 2014;112(11):1896-904. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114514002852.
Han LL, Wang YX, Li J, Zhang XL, Bian C, Wang H, et al. Gender differences in associations of serum ferritin and diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity in the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research. 2014;58(11):2189-2195. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201400088.
Al Akl NS, Khalifa O, Errafii K, Arredouani A. Association of dyslipidemia, diabetes and metabolic syndrome with serum ferritin levels: a middle eastern population-based cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. 2021; 1:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-03534-y.
Góth L, Rass P, Páy A. Catalase enzyme mutations and their association with diseases. Molecular Diagnosis. 2004;8(3):141-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03260057.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Esraa H. Oleiwi , Saba Z. Hussein

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.




















 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


