Mirabegron in the Management of Overactive Bladder Syndrome in Ghazi Al-Hariri Hospital
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad2451Keywords:
β3-adrenergic receptors, Bladder capacity, Mirabegron, Overactive bladder, Urinary incontinenceAbstract
Background: An individual’s quality of life is adversely affected by overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms. The key element that characterizes OAB is urgency which together with nocturia and urge urinary incontinence, are considered the most irksome symptoms. The side effects of the anticholinergic medication have caused a significant number of patients to discontinue their treatment. More recently, there has been research conducted on the potential correlation between an anticholinergic burden and the development of dementia. The detrusor muscle has been demonstrated to relax as a result of the activation of β3 adrenoceptors, which in turn facilitated the development of the first β3 adrenoceptor agonist. Mirabegron is the initial medication in this category to receive approval for the treatment of an overactive bladder.
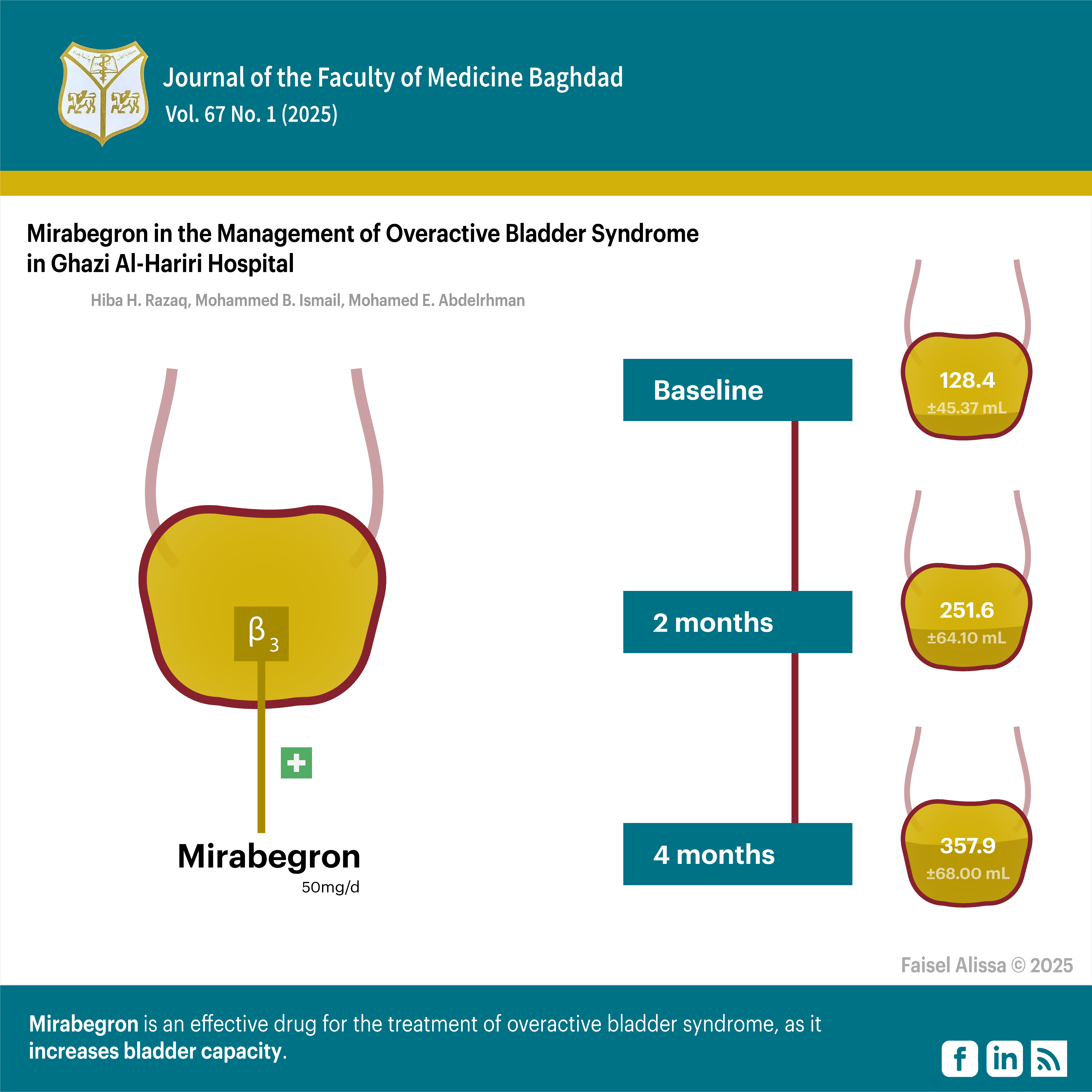
Objectives: To explore the effect of mirabegron on bladder capacity in patients with OAB.
Methods: A case series study was performed on 40 patients diagnosed with OAB from October 2023 to March 2024 in the Medical City Complex (Ghazi AL-Hariri Hospital) Urology Outpatient Clinic. These patients took a single dose of mirabegron 50 mg per day for four months and were assessed for the effect of this drug on the bladder capacity measurement, in milliliters, measured by ultrasound.
Result: Following treatment with mirabegron, a statistically significant increase in bladder capacity was found from the baseline level after two and four months.
Conclusion: Mirabegron is an effective drug for the treatment of OAB, as it increases bladder capacity.
Downloads
References
1. Hutchinson A, Nesbitt A, Joshi A, Clubb A, Perera M. Overactive bladder syndrome Management and treatment options. Aust J Gen Pract. 2020;49(9):593-8. https://doi.org/10.31128/AJGP-11-19-5142
2. Scarneciu I, Lupu S, Bratu O, Teodorescu A, Maxim L, Brinza A, et al. Overactive bladder: A review and update. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(6):1–8. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10879
3. Ismail MB, Abdullhussein WQ. Efficacy and safety of sacral neuromodulation in treatment of refractory overactive bladder. Indian J Forensic Med Toxicol. 2021;15(1):1315-21. https://doi.org/10.37506/ijfmt.v15i1.13597
4. Abbas IK, Rajab NA, Hussein AA. Formulation and in-vitro evaluation of darifenacin hydrobromide as buccal films. Iraqi J Pharm Sci. 2019;28(2):83-94. https://doi.org/10.31351/vol28iss2pp83-94
5. Leron E, Weintraub AY, Mastrolia SA, Schwarzman P. Overactive Bladder Syndrome: Evaluation and Management. Curr Urol. 2018;11(3):117-25. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447205
6.Sam P, Nassereddin A, LaGrange CA. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Bladder Detrusor Muscle. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482181/
7. Kennelly M, Wielage R, Shortino D, Thomas E, Mudd PN Jr. Long-term efficacy and safety of vibegron versus mirabegron and anticholinergics for overactive bladder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Drugs Context. 2022 Oct 10;11:2022-4-2.PMID: 36303599; PMCID: PMC9576010. https://doi.org/10.7573/dic.2022-4-2
8. Maggiore ULR, Cardozo L, Ferrero S, Sileo F, Cola A, Torella M, et al. Mirabegron in the treatment of overactive bladder. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2014;15(6):873-87. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2014.898752
9. Andersson KE. New developments in the management of overactive bladder: Focus on mirabegron and onabotulinumtoxinA. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2013;9(1):161-70. https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S33052
10. Kim JK, De Jesus MJ, Lee MJ, Dos Santos J, Dy JS, Ming JM, et al. β3-Adrenoceptor Agonist for the Treatment of Bladder Dysfunction in Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Urol. 2022;207(3):524-33. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000002361
11. Huang CK, Lin CC, Lin ATL. Effectiveness of antimuscarinics and a beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist in patients with overactive bladder in a real-world setting. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2020;10(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68170-4
12. Krhut J, Skugarevská B, Míka D, Lund L, Zvara P. Clinical Utility of β3-Adrenoreceptor Agonists for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder: A Review of the Evidence and Current Recommendations. Res Reports Urol. 2022;14(April):167-75.
https://doi.org/10.2147/RRU.S309144
13. Raju R, Linder BJ. Evaluation and Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Women. Mayo Clin Proc [Internet]. 2020;95(2):370-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.11.024
14. Sartori LGF, Nunes BM, Farah D, Oliveira LM De, Novoa CCT, Sartori MGF, et al. Mirabegron and Anticholinergics in the Treatment of Overactive Bladder Syndrome: A Meta-analysis. Rev Bras Ginecol e Obstet. 2022;45(6):337-46. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1770093
15. Mullen GR and Kaplan SA. Efficacy and Safety of Mirabegron in Men with Overactive Bladder Symptoms and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2021; 22 (1), 5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11934-020-01017-7
16. Kwon J, Kim DY, Cho KJ, Hashimoto M, Matsuoka K, Kamijo T. Pathophysiology of Overactive Bladder and Pharmacologic Treatments Including β3-Adrenoceptor Agonists -Basic Research Perspectives. Int Neurourol J. 2024 Feb;28(Suppl 1):12-33. Epub 2024 Feb 29. PMID: 38461853; PMCID: PMC10932578. https://doi.org/10.5213/inj.2448002.001
17. Almallah R and a Almukhtar H. Mirabegron-Induced Smooth Muscle Relaxation: Review of the Suggested Mechanisms. Iraqi Journal of Pharmacy 2023;20:195-200. https://doi.org/10.33899/iphr.2023.142851.1057
18. Schallom M, Prentice D, Sona C, Vyers K, Arroyo C, Wessman B, et al. Accuracy of measuring bladder volumes with ultrasound and bladder scanning. Am J Crit Care. 2020;29(6):458-67. https://doi.org/10.4037/ajcc2020741
19. Kim SC, Park M, Chae C, Yoon JH, Kwon T, Park S. Efficacy and tolerability of mirabegron compared with solifenacin for children with idiopathic overactive bladder: A preliminary study. Investig Clin Urol. 2021 May;62(3):317-323. Epub 2021 Mar 19. PMID: 33834641; PMCID: PMC8100008 https://doi.org/10.4111/icu.20200380
20. O'kane M, Robinson D, Cardozo L, Wagg A, Abrams P. Mirabegron in the Management of Overactive Bladder Syndrome. Int J Womens Health. 2022;14:1337-50. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJWH.S372597
21. Makhani A, Thake M, Gibson W. Mirabegron in the treatment of overactive bladder: Safety and efficacy in the very elderly patient. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 575-581. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S174402
22. Wagg A, Staskin D, Engel E, Herschorn S, Kristy R.M, Schermer CR. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of mirabegron in patients aged 65 yr with overactive bladder wet: A phase IV, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study (PILLAR). Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 211-220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.10.002
23. Krebs J, Pannek J, Rademacher F, Wöllner J. Real-World Effects of Mirabegron in Patients with Chronic Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity - A Retrospective Cohort Study. Res Rep Urol. 2020 May 22;12:187-192. https://doi.org/10.2147/RRU.S253713
24. Heintjes EM, Bezemer ID, Prieto-Alhambra D, Smits E, Booth HP, Dedman D, et al. Evaluating the effectiveness of an additional risk minimization measure to reduce the risk of prescribing mirabegron to patients with severe uncontrolled hypertension in four european countries. Clin Epidemiol. 2020;12:423–33. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S242065
25. Makhani A, Thake M, Gibson W. Mirabegron in the Treatment of Overactive Bladder: Safety and Efficacy in the Very Elderly Patient. Clin Interv Aging. 2020 Apr 23;15:575-581. PMID: 32368024; PMCID: PMC7185319. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S174402
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hiba H. Razaq, Mohammed B. Ismail, Mohamed E. Abdelrhman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


