Assessment of The Impact of Apremilast on Levels of IL-17, IL-23, and Lipids in Obese Psoriatic Patient
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbaghdad.6642260Keywords:
Apremilast, IL-17, IL-23, Obese, PsoriasisAbstract
Background: Psoriasis is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease with unknown aetiology that may be associated with the defect in proliferation and differentiation of the keratinocytes related to inflammatory cell infiltration. According to published reports, it is universal in occurrence; its prevalence in different populations varies from 0.1% to 11.8%. Receiving Apremilast resulted in a strong reduction in interleukin 17 and interleukin 23, as well as reduced expression of other inflammatory cytokines and improvement of psoriatic lesions.
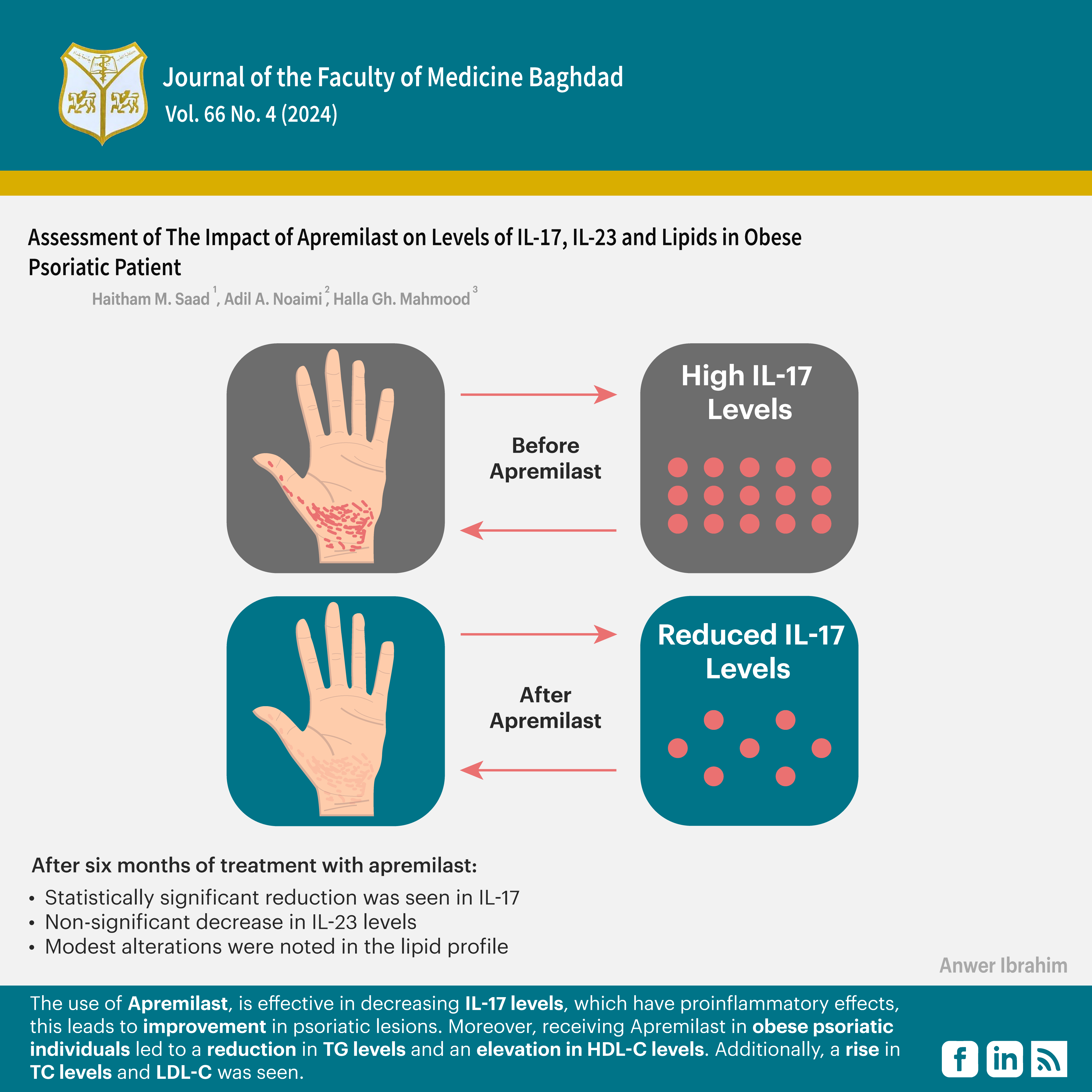
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the impact of Apremilast on levels of IL-17, IL-23, and lipids in obese psoriatic patients.
Methods: Thirty obese patients with psoriasis were included in this prospective interventional study to measure serum levels of lipid profile, IL-17, and IL-23, before and after receiving Apremilast treatment. A t-test was used to compare between means.
Results: The mean age of the participants was 38 years. The most common age group was 30–40 years. The levels of IL-17 before the administration of Apremilast were 225.55 ± 7.70 pg/mL. After six months of treatment with Apremilast, a statistically significant reduction was seen, with the value decreasing to 183.41 ±2.33 pg/ml. IL-22 levels before the administration of Apremilast were measured to be 76.42 ± 4.03 pg/mL. After six months of treatment with Apremilast, these levels exhibited a non-significant decrease to 67.15 ± 5.40 pg/ml. Modest alterations were noted in the lipid profile.
Conclusion: The use of Apremilast is effective in decreasing IL-17 levels, which have pro-inflammatory effects; this leads to improvement in psoriatic lesions. Moreover, receiving Apremilast in obese psoriatic individuals led to a reduction in TG levels and an elevation in HDL-C levels. Additionally, a rise in TC levels and LDL-C was seen.
Received: Nov., 2023
Revised: Oct., 2024
Accepted: Dec., 2024
Published: Dec., 2024
Downloads
References
1. Rajguru JP, Maya D, Kumar D, Suri P, Bhardwaj S, Patel ND. Update on psoriasis: A review. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care. 2020;9(1):20. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_689_19.
2. Thamer SM, Yahya MQ. The effect of lenalidomide ointment on TNF-α tissue levels in mice with imiquimod-induced psoriasis. JFacMedBaghdad. 2022;64(4):252-60. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.6441959 .
3. Ahmad A. A critical review of Daus-Sadaf (Psoriasis): Unani & modern perspectives. Int J Creat Res Thoug. 2020;8(7):4570-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.25897.83040
4. Al-Bidri KZ, Salman HA, Al-Hassan Y, Hasan MS. Fibromyalgia Syndrome in a sample of Iraqi patients with psoriasis. JFacMed Baghdad. 2014;56(1):49-52. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.561425
5. Sharquie KE, Noaimi AA, Alobaidi MH. A New Regimen in the Treatment of Psoriasis Using Oral Methotrexate. Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences, and Applications. 2019;9(02):165. https://doi.org/10.4236/jcdsa.2019.92014
6. Al-Ammari AM, Al-Attraqhchi AA, Al-Jibouri M. Species of Malassezia associated with psoriatic patients. JFacMed Baghdad. 2012;54(4):356-60. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.544704
7. AL-Sariay AH, Al-Ahmer SD, Muslim AM, Abood ZH, Haleem H. Genetic study of psoriasis disease: a review. Plant Archives. 2021;21(1):2046-8. https://doi.org/10.51470/PLANTARCHIVES.2021.v21.S1.335
8. Afra T, Razmi TM, Dogra S. Apremilast in psoriasis and beyond: big hopes on a small molecule. Indian Dermatology Online Journal. 2019;10(1):1. https://doi.org/10.4103/idoj.idoj_437_18
9. Milakovic M, Gooderham MJ. Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibition in psoriasis. Psoriasis: Targets and Therapy. 2021:21-9. https://doi.org/10.2147%2FPTT.S303634
10. Strober B, Alikhan A, Lockshin B, Shi R, Cirulli J, Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of efficacy in systemic-naive patients with moderate plaque psoriasis: pharmacodynamic results from the UNVEIL study. Journal of Dermatological Science. 2019;96(3):126-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2019.09.003.
11. Wang A, Bai Y. Dendritic cells: The driver of psoriasis. The Journal of Dermatology. 2020;47(2):104-13. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.15184
12. Mohammed RM, Hamid ZA. Assessment of Interleukin-17 levels in patients with hepatitis C viral infection. JFacMed Baghdad. 2024;66(1):39-44. https://doi.org/10.32007/jfacmedbagdad.2157
13. Mosca M, Hong J, Hadeler E, Hakimi M, Liao W, Bhutani T. The role of IL-17 cytokines in psoriasis. ImmunoTargets and therapy. 2021:409-18. https://doi.org/10.2147/ITT.S240891
14. Branisteanu DE, Cojocaru C, Diaconu R, Porumb EA, Alexa AI, Nicolescu AC, et al. Update on the etiopathogenesis of psoriasis. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2022;23(3):1-13. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2022.11124
15. Bugaut H, Aractingi S. Major role of the IL17/23 axis in psoriasis supports the development of new targeted therapies. Frontiers in immunology. 2021; 12:621956. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.621956
16. Lauffer F, Eyerich K, Boehncke WH, Asadullah K, Beissert S, Ghoreschi K, et al. Cytokines of the IL‐17 family in psoriasis. JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 2020;18(7):675-81. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddg.14124
17. Lé AM, Puig L, Torres T. Deucravacitinib for the treatment of psoriatic disease. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2022;23(6):813-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-022-00720-0
18. Mikhaylov D, Hashim PW, Nektalova T, Goldenberg G. Systemic psoriasis therapies and comorbid disease in patients with psoriasis: a review of potential risks and benefits. The Journal of clinical and aesthetic dermatology. 2019;12(6):46. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6624011/pdf/jcad_12_6_46.pdf
19. Gualtierotti R, De Lucia O. Efficacy and Metabolic Effect on Serum Lipids of Apremilast in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Case Report. 2019;8(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030398
20. Edwards CJ, Blanco FJ, Crowley J, Birbara CA, Jaworski J, Aelion J, et al. Apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in patients with psoriatic arthritis and current skin involvement: a phase III, randomised, controlled trial (PALACE 3). Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(6):1065-73. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207963
21. SAS S. Statistical Analysis System, User’s Guide. Statistical. Version 9.6. SAS Inst Inc Cary NC USA. 2018.
22. Woolcott OO, Seuring T. Prevalence trends in obesity defined by the relative fat mass (RFM) index among adults in the United States: 1999–2018. MetabClin Exp 2022; 128:155027. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.METABOL.2021.155027
23. Schafer P, Parton A, Capone L, Cedzik D, Brady H, Evans J, et al. Apremilast is a selective PDE4 inhibitor with regulatory effects on innate immunity. Cellular signalling. 2014;26(9):2016-29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.05.014
24. Schafer P. Apremilast mechanism of action and application to psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Biochemical pharmacology. 2012;83(12):1583-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.01.001
25. Parab S, Doshi G. An update on emerging immunological targets and their inhibitors in the treatment of psoriasis. International Immunopharmacology. 2022; 113:109341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109341
26. Ilowite NT, Laxer RM. Pharmacology: biologics. Textbook of pediatric rheumatology: Elsevier; 2016. p. 161-75. e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-24145-8.00013-2
27. Wu C, Rajagopalan S. Phosphodiesterase‐4 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for metabolic disorders. obesity reviews. 2016;17(5):429-41. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12385
28. Gualtierotti R, De Lucia O. Efficacy and metabolic effect on serum lipids of Apremilast in psoriatic arthritis: a case report. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019;8(3):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8030398
29. Blum S, Altman D. Treatment of generalized granuloma annulare with Apremilast: a report of 2 cases. JAAD case reports. 2019;5(11):976-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.09.015
30. Ferguson LD, Cathcart S, Rimmer D, Semple G, Brooksbank K, Paterson C, et al. Effect of the phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor Apremilast on cardiometabolic outcomes in psoriatic disease-results of the Immune Metabolic Associations in Psoriatic Arthritis study. 2022;61(3):1026-34. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab474
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Haitham M. Saad, Adil A. Noaimi, Halla Gh. Mahmood

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license..


